Artificial intelligence has fundamentally transformed how brands connect with consumers, enabling unprecedented capabilities to personalize experiences, predict behaviors, and optimize campaigns — at scale.
Yet with these powerful tools comes an equally powerful responsibility to use them ethically. The question facing modern marketers isn’t whether to embrace AI, but how to do so without crossing ethical boundaries.
The stakes couldn’t be higher. As consumers become increasingly aware of how their data is collected and used, trust has become the currency that determines long-term business success.
Brands that fail to implement ethical AI marketing practices risk not only regulatory penalties but also irreparable damage to their reputation and customer relationships.
This evolution requires marketers to navigate complex ethical terrain where innovation and responsibility must coexist. The challenge lies in distinguishing between legitimate persuasion and manipulative exploitation — a line that becomes increasingly blurred as AI capabilities advance.
Understanding these ethical considerations isn’t just about compliance; it’s about building sustainable marketing practices that benefit both businesses and consumers.
The foundation of ethical AI marketing
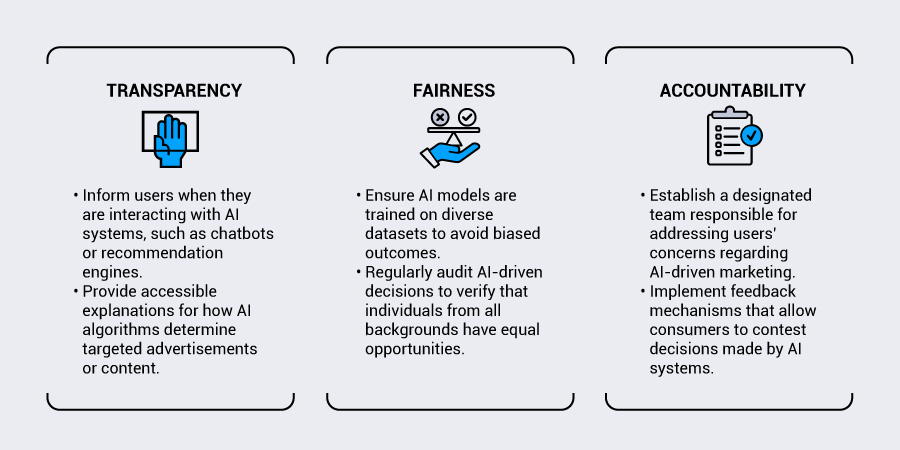
Ethical AI marketing requires commitment to several fundamental principles. Transparency stands as the cornerstone, requiring marketers to be clear about when and how AI influences consumer interactions.
This means disclosing AI-generated content, explaining automated decision-making processes, and providing consumers with meaningful choices about their data usage.
In addition to being an ethical best practice, disclosures about “automated decision-making” are required by an increasing number of data privacy laws around the world.
Fairness represents another critical pillar, demanding that AI systems treat all consumers equitably regardless of demographic characteristics.
This principle challenges marketers to examine their algorithms for bias and ensure that AI-driven targeting doesn’t perpetuate discrimination or exclusion. The goal is to create inclusive marketing experiences that serve diverse audiences without reinforcing harmful stereotypes.
Accountability completes this ethical framework by establishing clear responsibility for AI-driven marketing decisions. Organizations must designate oversight roles, implement review processes, and create mechanisms for addressing ethical concerns when they arise.
This systematic approach helps to ensure that ethical considerations remain central to AI marketing strategies rather than being treated as an afterthought.
Data privacy challenges in AI-driven marketing
The intersection of AI and data privacy presents one of the most complex ethical challenges in modern marketing. AI systems require vast amounts of consumer data to function effectively, creating tension between personalization benefits and privacy rights.
Marketers must find a way to respect consumer autonomy and maintain evolving regulatory compliance, while also executing effective marketing strategies.
Consumer consent has evolved beyond simple opt-in mechanisms to require ongoing, informed agreement for data usage. Ethical AI marketing demands that organizations explain not just what data they collect, but how AI systems will process and apply that information.
This level of transparency helps consumers make educated decisions about sharing their personal information.
Implementing privacy by design principles
Privacy by design principles provide a framework for embedding privacy considerations into AI marketing systems from the ground up. This approach requires marketers to minimize data collection to essential elements, implement strong security measures, and provide consumers with meaningful control over their information.
By building privacy protections into AI systems rather than adding them later, organizations demonstrate genuine commitment to ethical practices and potentially save themselves risk and headaches down the road.
Data minimization becomes particularly crucial when implementing ethical AI marketing strategies. Instead of collecting maximum possible data, responsible marketers focus on gathering only the information necessary to achieve specific, legitimate marketing objectives.
This approach reduces privacy risks while often improving AI system performance by eliminating irrelevant data points.
Addressing algorithmic bias in marketing AI
Algorithmic bias represents a significant threat to ethical AI marketing, potentially perpetuating discrimination and unfair treatment of different consumer groups.
These biases can emerge from training data that reflects historical inequalities, algorithm design choices, or the way AI systems interpret and apply learned patterns. Recognizing and addressing these biases requires ongoing vigilance and systematic intervention.
Marketing teams must actively audit their AI systems for discriminatory outcomes, examining whether certain demographic groups receive different treatment in targeting, pricing, or content delivery.
This process involves both technical analysis of algorithm performance and broader evaluation of marketing campaign results across diverse consumer segments. Regular bias testing should become a standard component of AI system maintenance and improvement.
Strategies for bias mitigation
Effective bias mitigation starts with diverse, representative training data that accurately reflects the full spectrum of target audiences. Marketers should examine their data sources for gaps or skews that might lead to biased outcomes and actively work to create more inclusive datasets.
This effort often requires intentional data collection strategies that ensure adequate representation of different demographic groups.
Algorithm design choices also play a crucial role in preventing bias. Marketers can implement fairness constraints that prevent AI systems from making decisions based on protected characteristics or from producing systematically different outcomes for different groups.
These technical safeguards must be combined with human oversight to ensure that fairness objectives are being met in practice.
The manipulation vs. persuasion spectrum
One of the most nuanced aspects of ethical AI marketing involves distinguishing between legitimate persuasion and manipulative exploitation. Traditional marketing has always involved persuasion, but AI’s ability to analyze individual psychological profiles and behavioral patterns raises new questions about where to draw ethical boundaries.
The key lies in understanding intent, impact, and consumer agency.
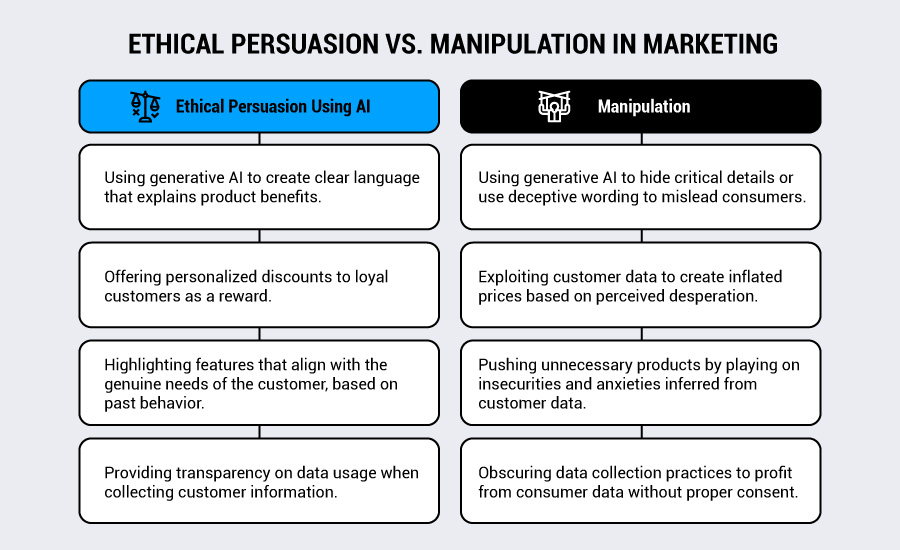
Ethical persuasion respects consumer autonomy while providing relevant, helpful information that enables informed decision-making. AI can enhance this process by delivering more personalized and timely content that genuinely serves consumer interests.
Conversely, manipulation exploits psychological vulnerabilities or emotional states to drive decisions that primarily benefit the marketer rather than the consumer. In addition to the ethical issues this creates, it’s a poor strategy for the goal of growing long-term customer relationships.
The distinction often comes down to whether AI marketing practices empower or diminish consumer choice. Ethical AI marketing should expand options and understanding, helping consumers make better decisions aligned with their genuine needs and preferences.
Manipulative practices, meanwhile, narrow options or create artificial urgency designed to bypass rational decision-making processes.
Identifying manipulative practices
Several warning signs can help marketers identify when AI-driven tactics cross into manipulative territory. Targeting based on emotional vulnerability — such as using divorce records to promote expensive financial products — represents a clear ethical violation.
Similarly, exploiting addiction patterns or mental health conditions through personalized marketing crosses important ethical boundaries.
Dynamic pricing that discriminates based on perceived financial desperation or location-based assumptions about spending power also raises serious ethical concerns.
While personalized pricing can offer legitimate benefits, it becomes manipulative when it exploits information asymmetries or takes advantage of circumstances beyond consumers’ control.
Building consumer trust through transparency
Trust serves as the foundation for sustainable AI marketing relationships, and transparency provides the pathway to building and maintaining that trust. Consumers increasingly expect clear communication about how AI influences their online experiences, from content recommendations to targeted advertisements.
Meeting these expectations requires proactive disclosure practices that go beyond minimal legal requirements.
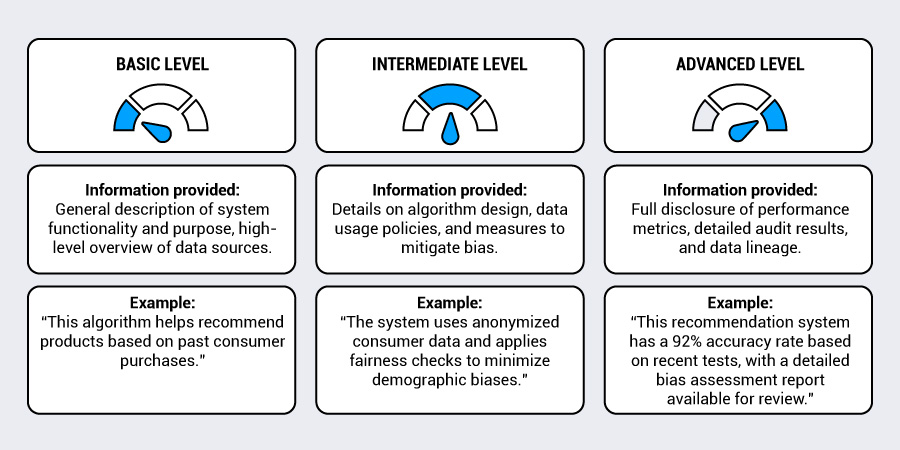
Effective transparency involves explaining AI decision-making in accessible language that consumers can understand without technical expertise. This means avoiding jargon and providing concrete examples of how AI systems work in practice.
Marketers should also provide easy access to information about data usage, algorithm functioning, and consumer rights regarding AI-driven marketing.
Implementing transparency frameworks
Successful transparency frameworks typically include multiple communication channels and varying levels of detail to accommodate different consumer preferences. Some consumers want comprehensive technical information, while others prefer simple, clear summaries of key points.
Providing both options helps to ensure that transparency efforts reach the broadest possible audience.
Regular transparency reports can help organizations demonstrate ongoing commitment to ethical AI marketing practices. These reports should include metrics on data usage, algorithm performance, bias testing results, and consumer feedback.
By making this information publicly available, organizations signal their commitment to accountability and continuous improvement.
Regulatory landscape and compliance considerations
The regulatory environment surrounding ethical AI marketing continues to evolve rapidly, with new laws and guidelines emerging in various jurisdictions.
Organizations must stay current with these developments while building flexible compliance systems for data privacy, AI use, and where they dovetail, that can adapt to changing requirements.
This dynamic landscape makes proactive ethical practices even more important for long-term success.
Current regulations like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California provide important foundations for ethical AI marketing, but they represent just the beginning of comprehensive regulatory frameworks.
Future regulations are likely to address AI-specific concerns, such as algorithmic transparency, bias prevention, and automated decision-making rights. The European Union has taken first steps with the AI Act. Preparing for these developments requires ongoing investment in ethical practices and compliance systems.
Preparing for future regulations
Forward-thinking organizations are implementing ethical AI practices that exceed current regulatory requirements, positioning themselves for success as regulations become more stringent.
This approach involves establishing internal ethical review processes, investing in bias detection and mitigation technologies, and creating comprehensive documentation of AI marketing practices.
Industry self-regulation also plays a crucial role in shaping ethical standards for AI marketing. Professional organizations and industry groups like the IAB and the AMA are developing best practice guidelines that help marketers navigate ethical challenges while maintaining competitive effectiveness.
Participating in these efforts demonstrates commitment to ethical leadership and helps shape industry standards.
Practical implementation strategies
Implementing ethical AI marketing requires systematic approaches that integrate ethical considerations into every aspect of marketing operations. This process begins with establishing clear ethical guidelines and policies that define acceptable practices and provide decision-making frameworks for marketing teams.
These guidelines should be specific enough to provide practical guidance while flexible enough to accommodate evolving technologies and circumstances.
Training and education represent critical components of successful implementation. Marketing teams need to understand both the technical capabilities of AI systems and the ethical implications of different usage approaches.
This education should be ongoing, reflecting the rapid pace of AI development and the evolution of ethical understanding in this field.
Creating ethical oversight systems
Effective oversight systems typically include cross-functional teams that bring together marketing professionals, legal experts, data scientists, and ethicists. These teams should regularly review AI marketing practices, assess potential ethical risks, and recommend improvements to existing systems.
The goal is to create sustainable processes that maintain ethical standards without stifling innovation. Regular auditing and assessment processes help organizations identify potential ethical issues before they become serious problems.
These audits should examine both technical system performance and broader marketing outcomes, looking for patterns of bias, unfair treatment, or manipulative practices. The results should inform ongoing system improvements and policy updates.
The business case for ethical AI marketing
Ethical AI marketing represents more than just compliance with regulations or moral obligations. It creates tangible business value through enhanced consumer trust, reduced legal risks, and improved long-term customer relationships.
Organizations that prioritize ethical practices often find that they can command premium pricing, achieve higher customer retention rates, and attract top talent who want to work for responsible employers.
Consumer research consistently shows that trust significantly influences purchasing decisions, with many consumers willing to pay more for products from companies they perceive as ethical and transparent.
This trend is particularly pronounced among younger consumers who have grown up with digital technology and are highly aware of privacy and ethical issues surrounding data usage.
Risk mitigation represents another crucial business benefit of ethical AI marketing. Organizations that implement strong ethical practices are better positioned to avoid regulatory penalties, consumer backlash, and reputational damage that can result from unethical AI usage.
The cost of prevention is typically much lower than the cost of remediation after ethical violations occur. And in the case of lost reputation and customer goodwill, there’s no guarantee they can be fully remediated.
Future directions for ethical AI marketing
The future of ethical AI marketing will likely involve increasingly sophisticated approaches to balancing innovation with responsibility. Emerging technologies such as federated learning, differential privacy, and explainable AI offer new possibilities for maintaining ethical standards while advancing marketing effectiveness.
These technologies enable more privacy-preserving data analysis and provide better visibility into AI decision-making processes.
Industry collaboration will play an increasingly important role in establishing and maintaining ethical standards. As AI marketing practices become more complex, individual organizations will benefit from sharing best practices, developing common standards, and creating industry-wide approaches to ethical challenges.
This collaboration can help establish consumer trust in AI marketing while enabling continued innovation.
The integration of ethical considerations into AI system design will likely become more sophisticated, with ethics by design becoming as important as privacy by design in system development.
This evolution will require closer collaboration between marketing teams, technologists, and ethicists to ensure that ethical considerations are built into AI systems from the ground up rather than added as afterthoughts.
Moving forward with ethical AI marketing
The path forward for ethical AI marketing requires commitment, vigilance, and continuous adaptation as both technology and ethical understanding evolve. Organizations that embrace this challenge will find themselves better positioned for long-term success in an increasingly conscious marketplace.
The key is to view ethical considerations not as constraints on marketing effectiveness but as essential components of sustainable business strategy.
Success in ethical AI marketing demands ongoing investment in people, processes, and technologies that support responsible practices. This includes training marketing teams on ethical principles, implementing robust oversight systems, and investing in technologies that enable ethical AI usage.
The organizations that make these investments early will gain competitive advantages that compound over time.
The conversation around ethical AI marketing will continue to evolve as new challenges emerge and our understanding of best practices develops. Staying engaged with this evolution through industry participation, ongoing education, and commitment to continuous improvement will be essential for maintaining ethical leadership in an AI-driven marketing landscape.