Every click, conversion, and campaign metric depends on your tags working correctly. When they don’t, you’re left with incomplete data and missed opportunities. Google Tag Assistant helps by providing you with insight into what’s happening with your tracking setup.
Google Tag Assistant is a set of tools that work together to give you full visibility into your tag implementation. Let’s talk about how to set it up and use it in a way that’s privacy-compliant.
What is Google Tag Assistant?
Tag Assistant helps you install and troubleshoot your Google tags, including Google Analytics, Google Ads, and Tag Manager. It examines your web pages and identifies which Google tags are present, then evaluates whether those tags are configured correctly and are firing as expected.
This unified approach addresses feedback from users who were juggling multiple tools for different debugging needs.
What is the Tag Assistant Chrome extension?
The Google Tag Assistant Chrome extension is the primary interface for this debugging tool. When clicked, the extension displays the Google tags found on the page in a side panel. You can simply navigate to any page on your website, click the extension icon, and instantly see which tags are active.
It works seamlessly with your existing workflow. There’s no need to leave your browser or switch among multiple tools. The Google Tag Assistant Chrome extension updates automatically as you browse different pages of your website.
Using Tag Assistant with Google Tag Manager (GTM)
If you’re using Google Tag Manager, the Tag Assistant extension becomes even more valuable. The Tag Assistant extension’s side panel enables you to see and check all the tags firing on your page, and the Troubleshoot button activates the debug mode using tagassistant.google.com.
This integration means you can debug your GTM container directly from the extension. You’ll see which tags are firing, when they fire, and whether they’re capturing the data you expect. This is particularly useful for complex setups in which multiple tags interact with each other.
Read more about Google Tag Manager and how it works with cookie consent and the GDPR.
Main functions and capabilities of Google Tag Assistant
The main function of Google Tag Assistant is to automatically check whether your Google tags have been implemented correctly. It identifies missing tags, incorrectly configured tags, and tags that might be firing multiple times. This validation happens in real time as you browse your website.
When tags aren’t working properly, Tag Assistant provides specific error messages and suggestions for fixes. That means instead of guessing what’s wrong, you’re working from clear feedback about what needs attention. The extension shows you how your tags are performing and which tags might be slowing down your website.
For websites using multiple Google products, Tag Assistant helps verify that all integrations are working together correctly. It’s helpful for setups involving Google Analytics, Google Ads, and Google Tag Manager working in combination.
The tool also helps identify potential privacy issues related to your tag configuration. While it’s not a complete privacy audit, it can highlight areas where your setup might not be respecting user consent preferences.
How to use Google Tag Assistant?
Using Google Tag Assistant involves several steps to help ensure your tags are implemented and functioning correctly:
- Install the extension: Download and install the Google Tag Assistant extension from the Chrome Web Store.
- Open your website: Navigate to any page on your website and click the Tag Assistant extension icon.
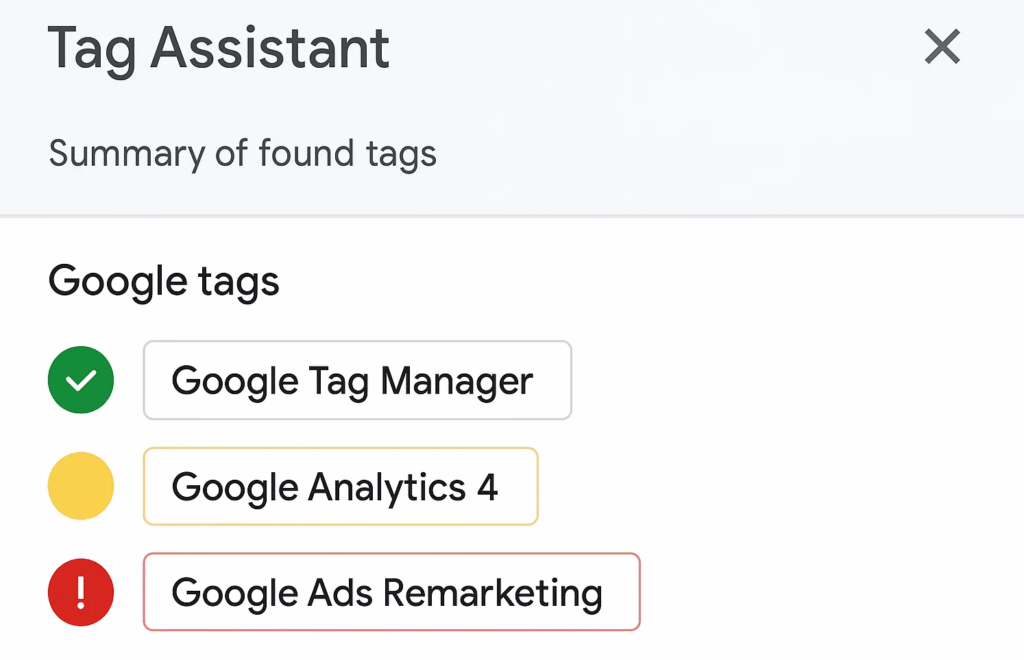
- Review detected tags: The side panel will display all detected Google tags on the page in a color indicating their status.
- Green: Tags are working correctly.
- Yellow or red: There are issues that need to be addressed.
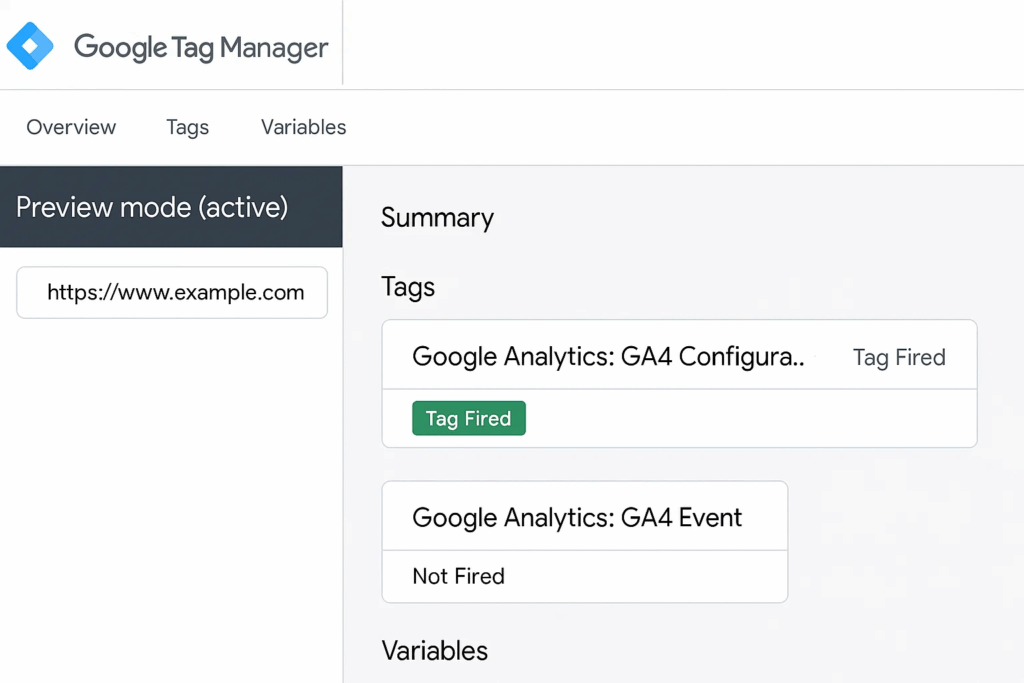
- Use debug mode: Click the Troubleshoot button to activate debug mode via tagassistant.google.com.
- This mode enables you to inspect how tags behave, even within iframes.
- It provides a centralized view of tag activity across your website.
- Test user interactions: Simulate typical user journeys, such as:
- Navigating through your conversion funnel
- Submitting forms
- Triggering specific events
The tool will show which tags fire and whether they capture the expected data.
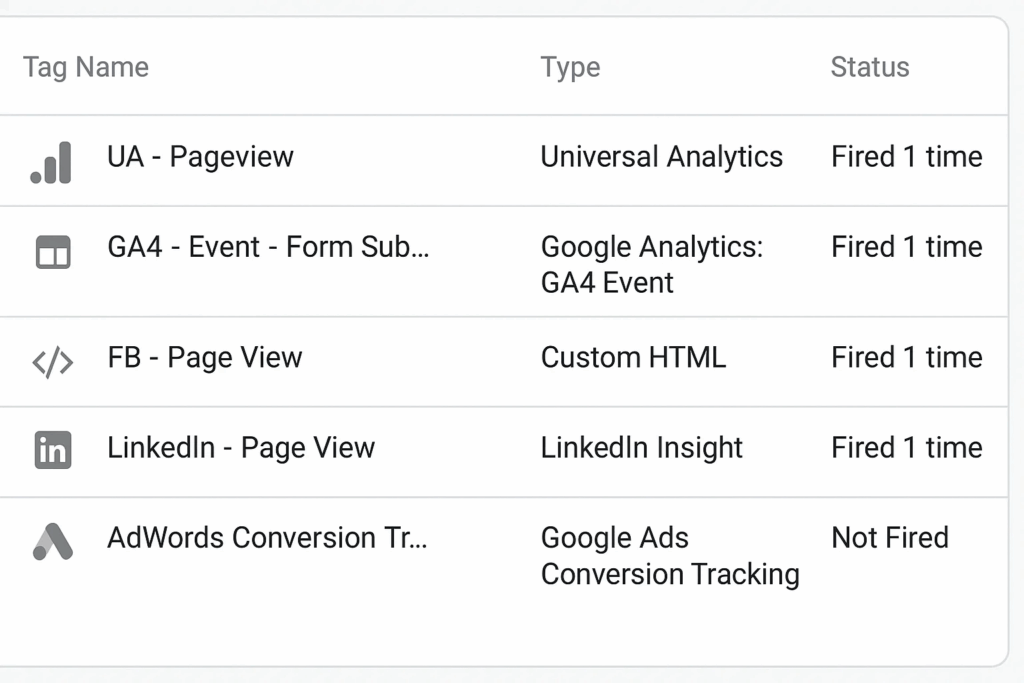
- Analyze tag details: Each tag entry includes information about its configuration and performance.
- Use this data to verify tag accuracy and optimize setup.
Interpreting results: What the tool reveals (and what it doesn’t)
Tag Assistant can tell you a lot, but it does have limitations you also need to be aware of. The tool shows which Google tags are active on each page and how they’re configured. You’ll see tag IDs, trigger conditions, and basic configuration parameters.
Tag Assistant also reveals the order in which tags fire and their timing relative to page load events, which can help you optimize tag performance and identify potential conflicts.
You can see what data each tag collects and when it sends information to Google’s servers. This visibility helps you verify that your tracking setup matches your expectations. The tool identifies common errors like missing parameters, incorrect tag IDs, or tags that fail to fire under certain conditions.
However, Google Tag Assistant has limitations. While it can identify some privacy-related issues, it doesn’t provide a comprehensive privacy audit.
You’ll need additional tools and expertise to achieve and maintain your compliance with regulations like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA).
The tool focuses specifically on Google tags, so if your website uses tags from other vendors, Tag Assistant won’t provide insights into their performance or configuration.
Additionally, Tag Assistant shows tag performance metrics, but doesn’t directly measure how tags affect user experience metrics like page load speed or user engagement. It primarily focuses on client-side tag behavior. If you’re using server-side tracking configurations, it provides limited visibility into those implementations.
Common tag errors and how to fix them
Tag Assistant is a valuable tool for diagnosing issues with your website’s tracking implementation. By recognizing common error patterns early, you can keep your data accurate and privacy-compliant.
Here are some frequent issues and how to address them.
Missing or incorrect tracking IDs
One of the most common issues Tag Assistant identifies is missing or mismatched IDs, such as Google Analytics measurement IDs or Google Ads conversion labels.
When these identifiers are wrong or absent, your tracking data won’t be routed correctly, which can lead to inaccurate reporting or missed conversions.
To fix this, double-check your tag settings against the IDs in your Google Analytics and Google Ads accounts. Whether you’re using Google Tag Manager or hardcoded tags, make sure each ID has been entered accurately.
To avoid this issue in the future, consider maintaining a centralized reference document with all your tracking IDs and their corresponding uses. Doing so can help reduce errors during implementation or updates.
Duplicate tag firing
Sometimes, the same tag is triggered more than once on a single page. Tag Assistant flags this as a potential problem because it can distort your analytics and waste ad spend.
Duplicate tag firing often results from duplicate tag placements or overlapping trigger settings in GTM. Conduct a thorough review of your tag setup to ensure each tag only fires once per intended action.
To keep things clean, use tag firing rules that explicitly prevent duplicate execution. GTM’s deduplication features can help manage this automatically.
Consent-related issues
Tag Assistant can detect when tags fire without user consent or continue to run after consent is withdrawn, both of which can pose compliance risks.
For more comprehensive consent support, implement a consent management platform (CMP) that integrates with your tag manager. This way, tags only activate when a user has provided appropriate consent.
For long-term consistency, choose a CMP that dynamically interacts with your tags and updates consent states in real time. This aligns all tracking activity with user preferences.
Is Tag Assistant enough for a privacy-conscious tracking setup?
Tag Assistant provides valuable insights, but it’s not sufficient for privacy-compliant tracking. That’s because the tool doesn’t verify whether tags are respecting user consent preferences.
You might see tags firing correctly from a technical perspective while they’re actually violating user privacy choices.
Tag Assistant doesn’t assess compliance with specific privacy regulations and won’t tell you if your tracking setup meets GDPR, CCPA/CPRA, or other regulatory requirements. The tool focuses on Google tags and provides limited insights into non-Google tracking technologies.
So while Tag Assistant shows tag performance metrics, it doesn’t directly measure how tags affect user experience or website performance from the user’s perspective.
For detailed privacy-conscious tracking, you need to implement consent management that controls tag firing based on user preferences. In addition, consider server-side tracking tools that provide better privacy control and data quality.
Why server-side tracking matters for privacy and performance
Server-side tracking represents an evolution in how websites collect and manage user data. When combined with client-side tools like Tag Assistant, it becomes a more privacy-friendly way to track.
Server-side tracking reduces data loss from ad blockers, browser restrictions, and user privacy settings. With more access to high quality data, you can make better decisions while respecting user privacy choices.
Moving tag processing to the server also reduces the number of scripts running in users’ browsers, which can improve website performance while maintaining comprehensive tracking capabilities.
Server-side tagging enables more control over how consent is processed because businesses can filter, enrich, and anonymize data before sharing it with third parties. That means you can implement privacy by design principles more effectively. However, privacy compliance still depends on the system being properly implemented.
Debugging: server-side vs. client-side tracking
Let’s look at the differences between server-side and client-side tracking so you can choose the right approach for your privacy and performance goals. Here’s how they compare:
Client-side tracking
| Pros | Cons |
| Easier to set up with tools like Google Tag Assistant | Relies on browser capabilities and user settings |
| Provides real-time visibility into user interactions | Vulnerable to ad blockers and privacy settings |
| Users can directly manage tracking through browser controls | Less control over how data is shared or processed |
| Faster iteration with browser-based debugging tools | Performance can be affected by multiple tracking scripts |
Server-side tracking
| Pros | Cons |
| Greater control over data privacy, filtering, and anonymization | Requires server infrastructure and technical expertise |
| Reduced impact from ad blockers and browser restrictions | More complex setup and maintenance |
| Improves website performance by reducing client-side load | Limited visibility into what’s happening in users’ browsers |
| Data is enriched and validated before reaching third-party services | Different debugging approach means browser tools often won’t apply |
Since both tracking options have benefits and drawbacks, many organizations are moving toward hybrid approaches that combine both methods.
Client-side tracking provides immediate visibility and user control, while server-side tracking offers better privacy management and data quality.
Reliable tag performance with server-side support
Combining client-side tools like Tag Assistant with server-side tracking creates a more complete and reliable tracking system.
Continue using Tag Assistant to monitor client-side tag behavior and verify that user-facing elements of your tracking system work correctly.
Implement server-side monitoring to track data processing, API calls, and server performance. This monitoring complements client-side insights and helps identify issues that might not be visible in either environment alone. Test data flow from client to server to support complete tracking functionality.
Use server-side logic to determine which tags should load for each user based on their consent preferences and browsing context. You can also validate and enrich data server-side to improve the quality of information sent to analytics and advertising platforms.
When you build server-side systems that automatically adjust data processing based on privacy choices, you respect consent preferences at every step.
Read more about the benefits of server-side tracking.
Finding the right balance of performance, accuracy, and privacy compliance
Google Tag Assistant is a valuable tool for checking and debugging your website’s tracking setup. It helps reduce downtime, enables your tags to fire correctly, and gives you quick visibility into what’s working and what’s not. But it’s just one part of a privacy-conscious tracking strategy.
To get the most out of your tracking, combine client-side tools like Tag Assistant with server-side tracking solutions. While Tag Assistant gives you fast feedback and validation, server-side setups offer better privacy control, improved data quality, and more flexibility.
Add a solid consent management layer, and you’ve got a system that respects user privacy while still giving you the insights your business needs.
In short, Tag Assistant is a good starting point, but paired with server-side tracking, it becomes part of a much more powerful and future-ready solution.


