Attribution tracking: How to track and attribute conversions in a privacy-focused world
Marketing campaigns typically run across multiple channels, but many companies are unable to say which channel is driving conversions. This is because traditional attribution tracking has relied on third-party cookies and cross-site tracking — methods that browsers are now blocking and privacy laws are restricting.

Attribution tracking remains essential for understanding which channels deliver results, how customers move through your funnel, and where your budget has the most impact.
While there are various methods to track attribution, new privacy-first methods are making it possible to gain these insights, and to do so without relying on outdated tracking techniques or compromising user trust.
What is attribution tracking?
Attribution tracking measures the contribution of each marketing touchpoint to a conversion throughout the customer journey. It answers the fundamental question: Which marketing activities drive results?
At its core, attribution tracking connects user interactions with your ads, content, and campaigns to specific outcomes like purchases, signups, or downloads. This process involves collecting data about touchpoints, analyzing their relationships to conversions, and assigning credit to different marketing channels.
The challenge lies in tracking users across devices and platforms while respecting their privacy choices. Traditional attribution relied heavily on tracking cookies and cross-site tracking, methods that are increasingly restricted or blocked entirely.
What is cross-channel attribution tracking?
Cross-channel attribution tracking maps user interactions across multiple marketing channels and touchpoints. Instead of viewing each channel in isolation, it creates a unified view of how email, social media, paid search, display advertising, and other channels work together to drive conversions.
This approach recognizes that customers rarely convert after a single touchpoint. They might discover your brand through social media, research products via organic search, receive email nurture campaigns, and finally convert through a paid ad. Cross-channel attribution helps you understand this complex journey and allocate budget accordingly.
Why is attribution tracking important?
Understanding attribution web analytics and their impact goes beyond basic campaign reporting. At its core, attribution tracking takes the guesswork out of your marketing efforts.
But there’s more. Here are four reasons attribution tracking matters for your marketing strategy.
Budget allocation becomes data-driven
Attribution tracking shows which channels generate the highest return on investment, helping you shift spend toward the most effective touchpoints. Without this insight, you might overinvest in channels that appear successful but don’t actually drive conversions.
Campaign optimization improves significantly
Using ad attribution tracking, you can understand which creative elements, audience segments, and messaging drive results, and you can refine campaigns for better performance. Attribution data reveals patterns that aren’t visible in channel-specific reporting.
Customer journey insights become clearer
Attribution tracking exposes how customers interact with your brand over time. You might discover that display ads don’t drive immediate conversions but play a crucial role in initial awareness, changing how you measure and optimize these campaigns.
Marketing accountability increases
Clear attribution helps demonstrate marketing’s impact on business outcomes. This transparency builds trust with stakeholders and supports budget requests for successful channels.
Attribution tracking methods
Attribution tracking methods define which user interactions are eligible for conversion credit. These approaches aren’t attribution models — like first-click or last-click — they’re the foundational decisions about which actions and events get tracked in the first place.
Think of it this way: attribution methods answer “Which user actions count?” while attribution models answer “How do we distribute credit among those actions?” Understanding these approaches helps you choose the right tracking strategy for your business needs.
The following are common attribution tracking methods.
View-through attribution
View through attribution credits conversions to ads that users saw but didn’t click. This method recognizes that exposure to advertising can influence purchasing decisions even without direct interaction.
For example, a user might see your display ad on a news website, then later search for your brand directly and make a purchase. View through attribution would credit the original display ad for contributing to that conversion, even though the user didn’t click on it.
This tracking method typically uses impression tracking pixels and sets attribution windows — usually 1–7 days — during which post-impression conversions are credited to the original ad. The challenge with view-through attribution lies in proving causation rather than correlation, as users might have converted anyway.
Click-through attribution
Click-through attribution tracks conversions that result from users clicking on ads or marketing content. This method creates a direct link between user actions and subsequent conversions.
When someone clicks your Google ad and purchases within your attribution window, click-through attribution assigns credit to that paid search campaign. This approach provides clearer causation signals than view through attribution since it tracks explicit user engagement.
The limitation of focusing solely on click-through attribution is that it undervalues awareness-building activities like display advertising, video campaigns, and social media.
Click attribution
Click attribution specifically measures the impact of users clicking on various elements within your marketing campaigns. This includes tracking clicks on email links, social media posts, website buttons, and other interactive elements.
Unlike broader click-through attribution, click attribution can track multiple click events within a single customer journey. It helps you understand which specific content pieces, calls-to-action, or campaign elements drive engagement and subsequent conversions.
This granular approach to attribution tracking provides insights into content performance and user behavior patterns that inform both creative strategy and user experience optimization.
Impression attribution
Impression attribution analyzes how ad exposures influence user behavior, even without clicks or direct interactions. This method tracks when users see your ads and measures subsequent conversion activity within defined time windows.
Impression attribution proves particularly valuable for brand awareness campaigns and display advertising. Where the goal extends beyond immediate conversions to include brand recall and consideration. It helps demonstrate the value of upper-funnel marketing activities that traditional last-click attribution often overlooks.
The effectiveness of impression attribution depends on accurately measuring genuine ad visibility — not just ad serving — and establishing reasonable attribution windows that reflect your typical customer journey length.
Engagement-based attribution
Engagement-based attribution tracks various user interactions beyond simple clicks and impressions. This method captures scroll depth, video watch time, social media engagement, email opens, and other meaningful interactions that indicate user interest.
This approach recognizes that engagement signals often predict conversion likelihood better than basic click-through metrics. A user who watches 75% of your video ad or spends significant time engaging with your social media content shows higher intent than someone who merely saw an impression.
Engagement-based attribution proves particularly valuable for content marketing and social media campaigns where traditional click-through attribution might undervalue performance. By tracking micro-engagements, you can identify which content resonates with audiences and drives downstream conversions.
Cross-device attribution
Cross-device attribution connects user actions across smartphones, tablets, desktops, and other devices to create unified customer journey insights. This method addresses the reality that customers often research on mobile devices and convert on desktop, or vice versa.
The challenge lies in connecting anonymous sessions across devices without invasive tracking. Solutions include authenticated user tracking (when users log in across devices), probabilistic matching based on behavioral patterns, and deterministic linking through email addresses or other identifiers.
Cross-device attribution becomes essential as customer journeys span multiple touchpoints and devices. Without this capability, you might undervalue mobile advertising that drives desktop conversions or miss opportunities to optimize cross-device user experiences.
Offline attribution
Offline attribution connects online marketing activities to in-store purchases, phone calls, and other offline conversions. This method bridges the gap between digital campaigns and real-world business outcomes.
Implementation typically involves store visit tracking, phone call attribution, promo code usage, and customer survey data that links online exposure to offline actions. Some solutions use location data to determine when users who saw online ads subsequently visit physical store locations.
Offline attribution proves crucial for businesses with physical locations or phone-based sales processes. It helps demonstrate the full value of digital marketing beyond online conversions and supports budget allocation decisions that account for omnichannel customer behavior.
Examples of attribution tracking
Attribution tracking looks different for every business. It depends on your model, customer journey, and the tools you have in place. Below are examples of how companies put multi-channel attribution and campaign tracking strategies into action across different platforms and channels.
The goal is to align your approach with how your customers actually convert. A mobile app company will need very different insights than a B2B software provider or a retail brand with brick-and-mortar stores.
Mobile app attribution tracking
Mobile app tracking attribution connects app installs and in-app events to their originating marketing campaigns. This process involves tracking users from initial ad exposure through app store visits, downloads, and subsequent in-app actions.
App attribution tracking faces unique challenges, like how privacy-related changes to Apple’s iOS that were introduced with version 14.5 have limited cross-device tracking capabilities.
Solutions like Apple’s SKAdNetwork provide privacy-preserving attribution for iOS campaigns, while Google’s Android attribution relies on Google Play Install Referrer and other privacy-compliant methods.
Mobile attribution tracking typically measures:
- Install attribution from various traffic sources
- Post-install event tracking (purchases, registrations, level completions)
- User lifetime value attribution
- Re-engagement campaign attribution for existing users
Google Ad attribution tracking
Google Ads attribution tracking measures how search, display, shopping, and video campaigns contribute to conversions across the customer journey. Google’s attribution models range from simple last-click attribution to sophisticated data-driven attribution that uses machine learning.
Google’s Enhanced Conversions feature improves attribution accuracy by using first-party customer data to link conversions back to ad interactions. This approach works particularly well in a privacy-first environment because it relies on data customers willingly share rather than tracking cookies.
The platform’s attribution reporting shows assisted conversions, path length analysis, and time lag reports that reveal how different campaigns work together. This data helps optimize bidding strategies and budget allocation across campaign types.
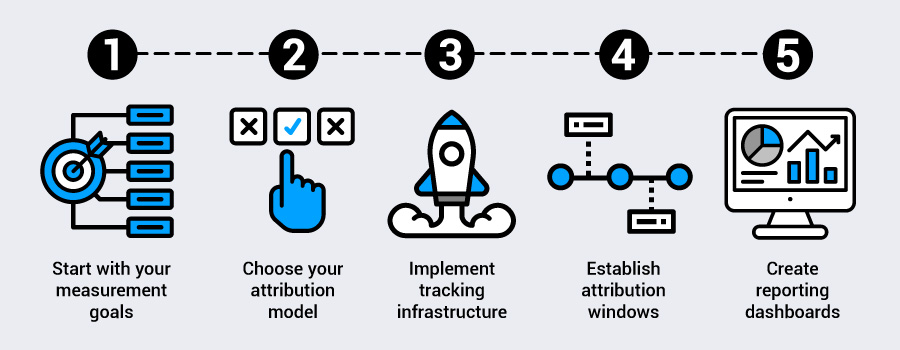
How to set up an attribution tracking system?
Building an effective attribution tracking system requires careful planning and the right technology stack. Here’s how to approach implementation.
1. Start with your measurement goals
Define what conversions matter most to your business and establish marketing key performance indicators. Consider both immediate conversions and longer-term customer lifetime value when setting up your tracking framework.
Do you know what KPIs to measure? Discover the top marketing KPIs for privacy-conscious marketers.
2. Choose your attribution model
Decide whether first-click, last-click, linear, time decay, or data-driven attribution best fits your business model and customer journey patterns. Many businesses start with last-click attribution and evolve toward more sophisticated models as they gather data.
Learn more about attribution models and which one to implement for your business.
3. Implement tracking infrastructure
Set up conversion tracking pixels, configure Google Analytics goals, and ensure your customer relationship management system captures attribution data. Consider server-side tracking solutions that improve data accuracy and privacy compliance.
4. Establish attribution windows
Define how long after exposure or interaction you’ll credit campaigns for conversions. These windows should reflect your typical sales cycle length and customer consideration periods.
5. Create reporting dashboards
Build reports that show attribution insights in actionable formats. Include assisted conversions, channel interaction analysis, and return on ad spend calculations that inform optimization decisions.
Attribution tracking software
Attribution tracking isn’t a manual process, and there are many attribution tracking software options on the market. Your choice will depend on your company size, technical capabilities, and privacy requirements.
Here are the key categories to consider.
- Enterprise attribution platforms like Adobe Analytics, Salesforce Marketing Cloud, and HubSpot offer comprehensive attribution tracking with advanced modeling capabilities. These solutions integrate with multiple data sources and provide sophisticated analysis tools.
- Specialized attribution tools such as Singular, AppsFlyer, and Branch focus specifically on attribution measurement. They typically offer more detailed attribution features than general analytics platforms but require additional integration work.
- Built-in platform attribution from Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager, and other advertising platforms provides campaign-specific attribution insights. While limited to single-platform analysis, these tools offer easy implementation and direct campaign optimization features.
- Privacy-first solutions, such as those from Usercentrics, are emerging to prioritize user consent and data protection while maintaining attribution capabilities. These tools work within browser restrictions and privacy regulations to support privacy-compliant measurement.
The role of server-side tracking in attribution
Server-side tracking fundamentally changes how attribution data is collected and processed. Instead of relying on browser-based tracking that can be blocked or restricted, server-side solutions move data collection to secure server environments.
This approach offers several advantages for attribution tracking. First, it reduces data loss from ad blockers and browser restrictions that commonly affect client-side tracking. Second, it provides more control over data collection and processing, enabling better privacy compliance and data quality.
Server-side tracking also enables more sophisticated attribution modeling. With access to complete, unfiltered data sets, marketers can implement advanced attribution algorithms that account for complex customer journeys and multi-touch interactions.
The shift to server-side tracking requires technical implementation but offers more reliable attribution insights in a privacy-focused environment. It represents a fundamental change in how attribution data flows from user interactions to marketing insights.
How server-side tracking improves attribution tracking
Server-side tracking addresses several limitations that affect traditional attribution tracking accuracy and reliability.
Data completeness improves significantly
Browser-based tracking often loses data due to ad blockers, cookie restrictions, and client-side errors. Server-side tracking captures more complete data sets by processing information in controlled server environments.
Cross-device attribution becomes more reliable
Server-side solutions can better connect user actions across devices and platforms by using first-party identifiers and authenticated user data rather than relying on third-party cookies.
Attribution windows extend effectively
Without browser storage limitations, server-side tracking can maintain longer attribution windows and more complex customer journey analysis. This capability proves especially valuable for businesses with extended sales cycles.
Privacy compliance strengthens
Server-side tracking provides better control over data collection and processing, making it easier to respect user consent choices and comply with privacy regulations while maintaining attribution capabilities.
Integration capabilities expand
Server-side solutions can connect multiple data sources — from advertising platforms to customer relationship management systems — creating more comprehensive attribution insights than siloed tracking approaches.
These advantages show how server-side tracking can improve the quality and reliability of attribution. But putting them into practice — especially while meeting privacy requirements — often requires support from tools that manage consent and data processing effectively.
Benefits of attribution with Usercentrics server-side tracking
Usercentrics Server-Side Tagging (SST) is designed to help teams implement server-side tracking in a way that supports attribution while staying aligned with consent requirements and data privacy standards.
Accurate attribution with privacy safeguards
By processing data on the server, SST helps reduce data loss from ad blockers and browser restrictions. It works only with consented data and aligns with privacy requirements, supporting attribution tracking without overstepping user preferences.
Consent signal integration
Usercentrics SST integrates directly with the consent management platform. When a user’s consent status changes, the tracking setup updates automatically. This reduces the complexity of managing consent manually across systems and ensures attribution reflects actual user permissions.
Support for data-driven attribution (DDA)
Our server-side tracking solution provides the clean, comprehensive data sets that advanced attribution models require. Data-driven attribution algorithms perform better with complete, unfiltered data, which is exactly what server-side tracking delivers.
Attribution tracking that respects user privacy
Attribution tracking doesn’t have to be a choice between accuracy and privacy compliance. The most successful marketers are building measurement systems that deliver reliable insights while respecting user choices and regulatory requirements.
Server-side tracking, first-party data strategies, and consent-based measurement provide the foundation for sustainable attribution tracking. These approaches give you the campaign insights you need while building user trust through transparent data practices.
Your attribution strategy should evolve with privacy regulations, not fight against them. By choosing privacy-first solutions now, you’re building measurement capabilities that will remain effective as browsers and regulations continue restricting traditional tracking methods.
