Google Analytics server-side tracking explained: benefits and step-by-step setup
Google Analytics server-side tracking is quickly becoming a must-have for businesses that need accurate, privacy-compliant analytics. Server-side tagging offers a way to regain control over your data and future-proof your marketing strategy.
Instead of sending tracking information directly from a user’s browser to Google Analytics, server-side tracking routes the data through your own server first. This extra step gives you more control over data quality, supports compliance with privacy regulations, and helps reduce data loss from ad blockers and browser restrictions.
So, let’s talk about how Google Analytics server-side tracking works and how to set it up step-by-step using Google Tag Manager and GA4.
Google Analytics 4 and server-side tracking: what you need to know
The shift to server-side tracking represents more than just a technical change; it’s a fundamental rethinking of how web analytics works. With traditional client-side tracking, data collection happens in browsers, which can significantly restrict data access and flow. Server-side tracking puts you back in control.
When you implement Google Analytics 4 server-side, your website sends collected data to your servers instead of directly to Google. Your server then processes this data and forwards relevant information to GA4 using the Measurement Protocol API. This two-step process might seem more complex, but it solves several important problems associated with traditional tracking methods.
The Measurement Protocol API accepts the same event data that would normally come from browser scripts, but processes it through your infrastructure. You send HTTP requests containing event parameters, user identifiers, and measurement data.
Your server then becomes the gatekeeper that validates, cleans, and forwards information based on your business rules and privacy requirements.
Differences from Universal Analytics setup
Universal Analytics was not made with server-side tracking in mind, which complicated the process. You could send data, but then companies would lose enhanced ecommerce features and audience capabilities.
GA4 fixed these limitations. Server-side and client-side events work the same way in reports. You can build audiences, set up conversions, and access all platform features regardless of how you collect the data.
Key benefits of using Google Analytics with server-side tagging
Server-side web analytics addresses several limitations that plague traditional tracking methods. The benefits extend beyond just data collection. Server-side analytics tracking impacts your entire analytics strategy.
Improved data accuracy and control
Ad blockers affect roughly 25 percent of web traffic, which can cause significant gaps in your analytics. When you compare server-side vs client-side analytics, there’s a clear winner when it comes to data completeness. Server-side web analytics bypass these restrictions entirely because the data flows directly from your servers to Google Analytics.
You also gain more control over data quality. Instead of accepting whatever the browser sends, you can validate events, clean up parameters, and ensure consistent formatting before forwarding to GA4.
Greater user privacy and data privacy compliance
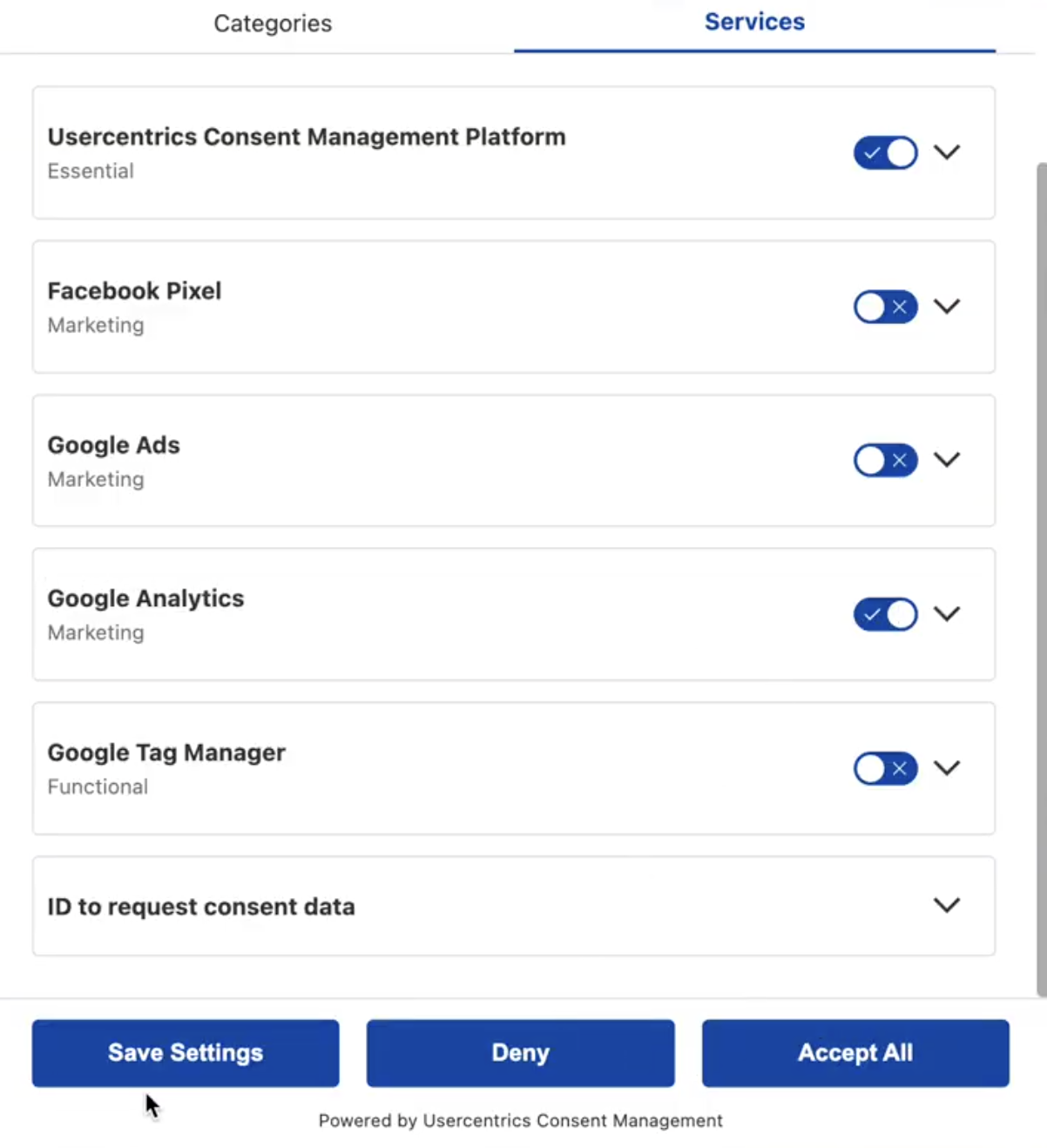
Many privacy regulations, such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), require explicit consent before collecting personal data. Server-side tracking enables you to apply consent preferences at the server level. That means that data only flows to Google Analytics from users who have opted in.
This approach also supports data minimization and limits transmission of personally identifiable information (PII). You can strip out sensitive details, hash email addresses, or anonymize IP addresses before sending data to third parties.
Reduced data loss from ad blockers and browser restrictions
Apple’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) and similar browser features limit how long tracking cookies persist. Server-side analytics tracking extends cookie lifetimes because the data processing happens on your domain rather than through third-party scripts.
Safari’s ITP limits client-side cookies to seven days for cross-site tracking. Server-side tracking can maintain user identification for much longer periods, which improves attribution accuracy for longer sales cycles.
Faster load times
Attribution modeling relies on your ability to connect user actions over time. When cookies expire prematurely, you’re no longer able to attribute conversions to earlier touchpoints in the customer journey.
Server-side tracking maintains first-party cookies for extended periods, often up to two years instead of the seven-day limit imposed by browser restrictions. This extended timeline provides more accurate attribution data for your marketing campaigns.
Learn more about the benefits of server-side tracking.
How to set up Google Analytics server-side tracking
Setting up GA4 server-side tracking isn’t something you can flip on with a single switch. It requires some planning and technical configuration.
The process involves three main stages: preparing your infrastructure, sending data from the client to your server, and then forwarding that data to Google Analytics.
Prerequisites and tools
Before you dive into implementation, make sure you have the following in place:
- Google Tag Manager server container: This acts as the core infrastructure for processing and routing your analytics data. You can host it on Google Cloud Platform (the default), your own servers, or other cloud providers.
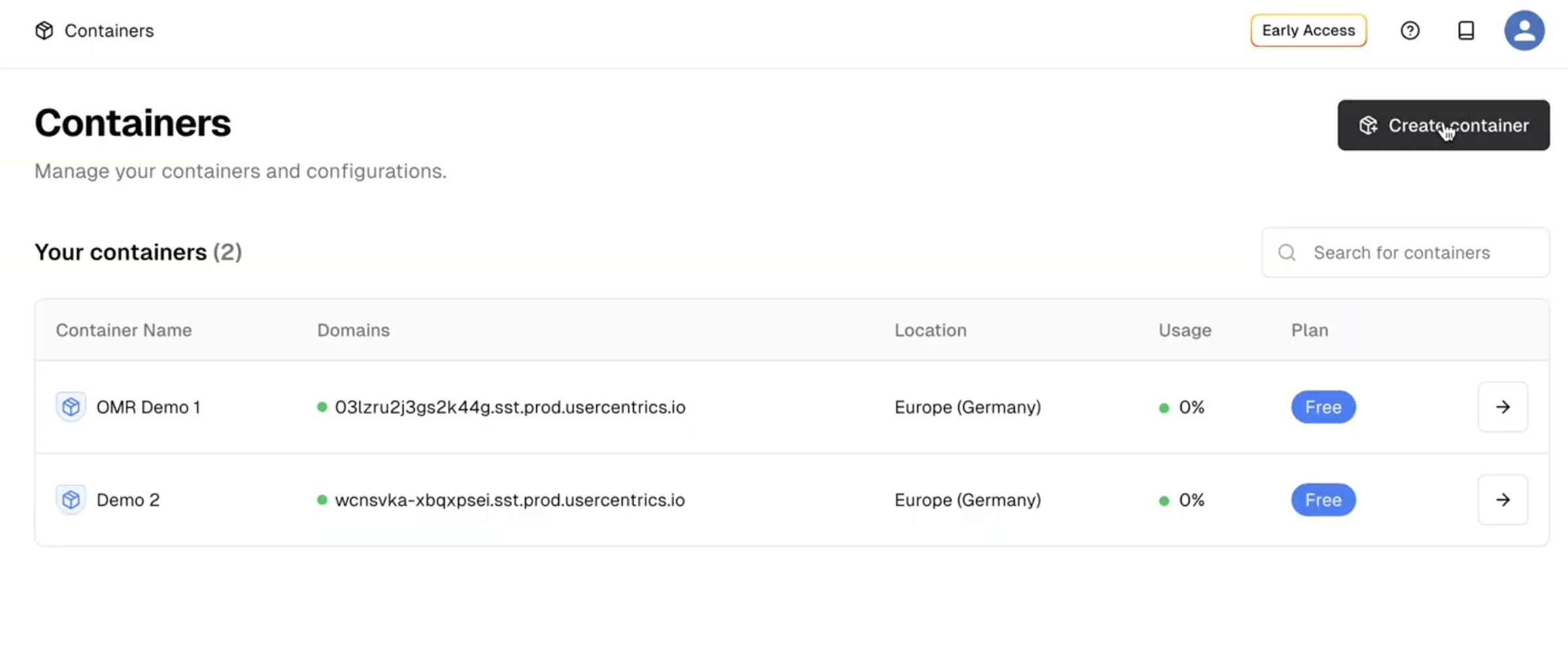
- Custom domain: For first-party cookie status, the server container should run on a subdomain of your website (e.g. analytics.yoursite.com.)
- GA4 property: Confirm that your GA4 property is configured with the events, parameters, and conversions you want to track.
- Development resources: Server-side tagging isn’t a plug-and-play setup. You’ll need developers familiar with web tracking, server management, and API integrations.
Once these foundations are in place, you can begin the actual implementation process.
Sending data from the client to your server endpoint
The first step is to redirect event data from the browser to your server container instead of sending it straight to Google Analytics. You’ll need to:
- Update your GA4 tracking code: Replace the standard GA4 script with a version that points to your server endpoint. Functionally, the client-side code still gathers events (page views, clicks, conversions, etc.) but it routes them through your custom domain.
- Leverage the data layer: Configure your website’s data layer so that all relevant events and parameters are included. This helps ensure that your server receives a complete, structured picture of user interactions.
In short, you’re inserting your own server as a “middleman” between the client and Google Analytics.
Forwarding hits from your server to Google Analytics
Once the data arrives at your server container, it needs to be processed and sent on to GA4 using the Measurement Protocol API. This is where most of the configuration happens:
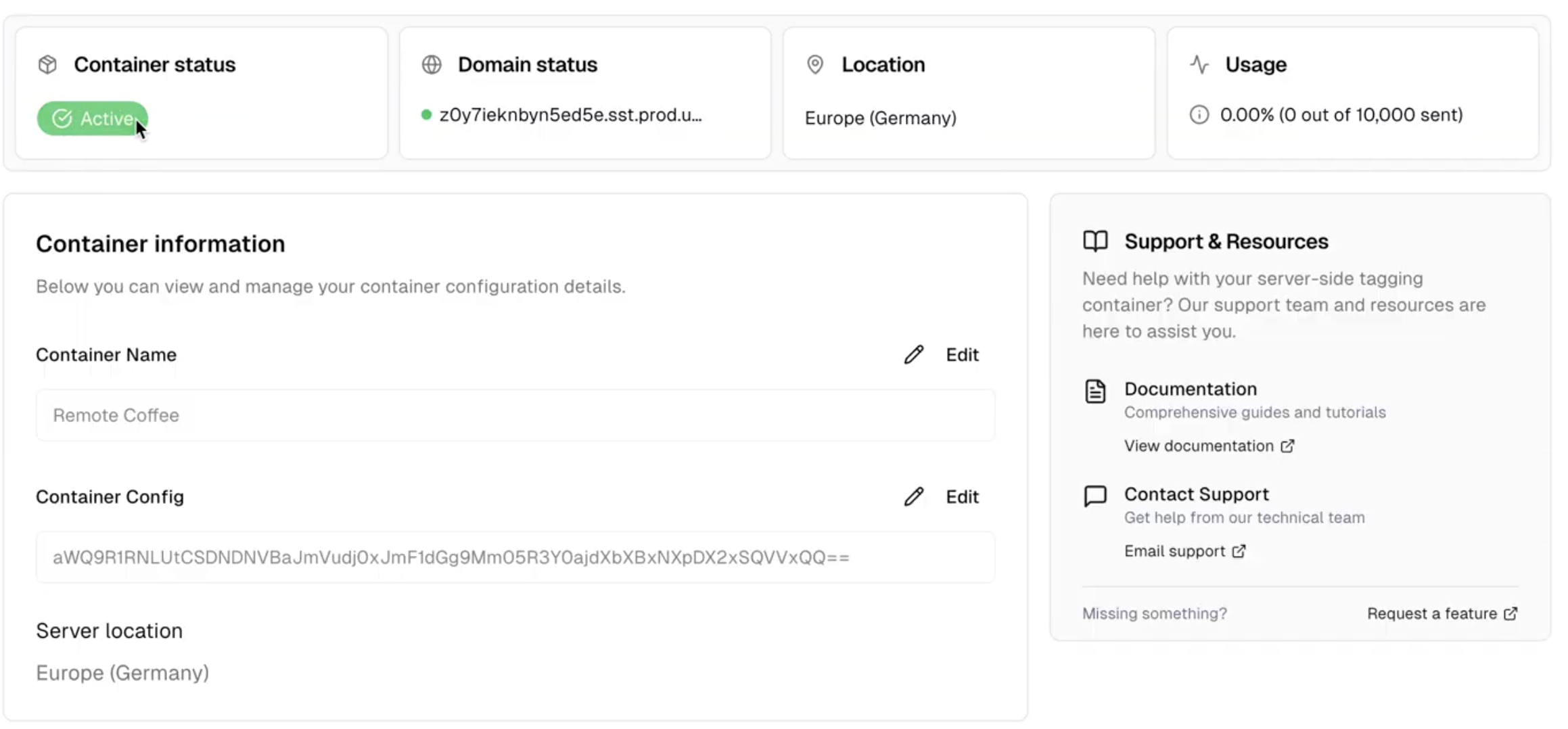
- Set up a GA4 client in Google Tag Manager (GTM): This client listens for incoming requests from your site and interprets them in a way your server can handle.
- Create server-side tags: These tags format the data correctly and forward it to Google Analytics. They also give you the opportunity to apply transformations (e.g. anonymizing IPs, enriching data, or filtering out noise.)
- Implement consent logic: Respect user privacy by ensuring that only those who have opted in are tracked. This is especially important for compliance with the GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations.
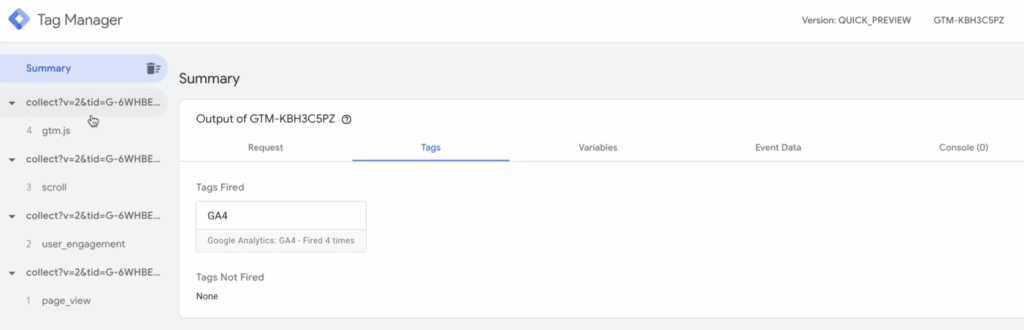
- Thoroughly test your setup: Use the GTM preview mode and GA4 debug tools to confirm that events are flowing as expected and reporting correctly.
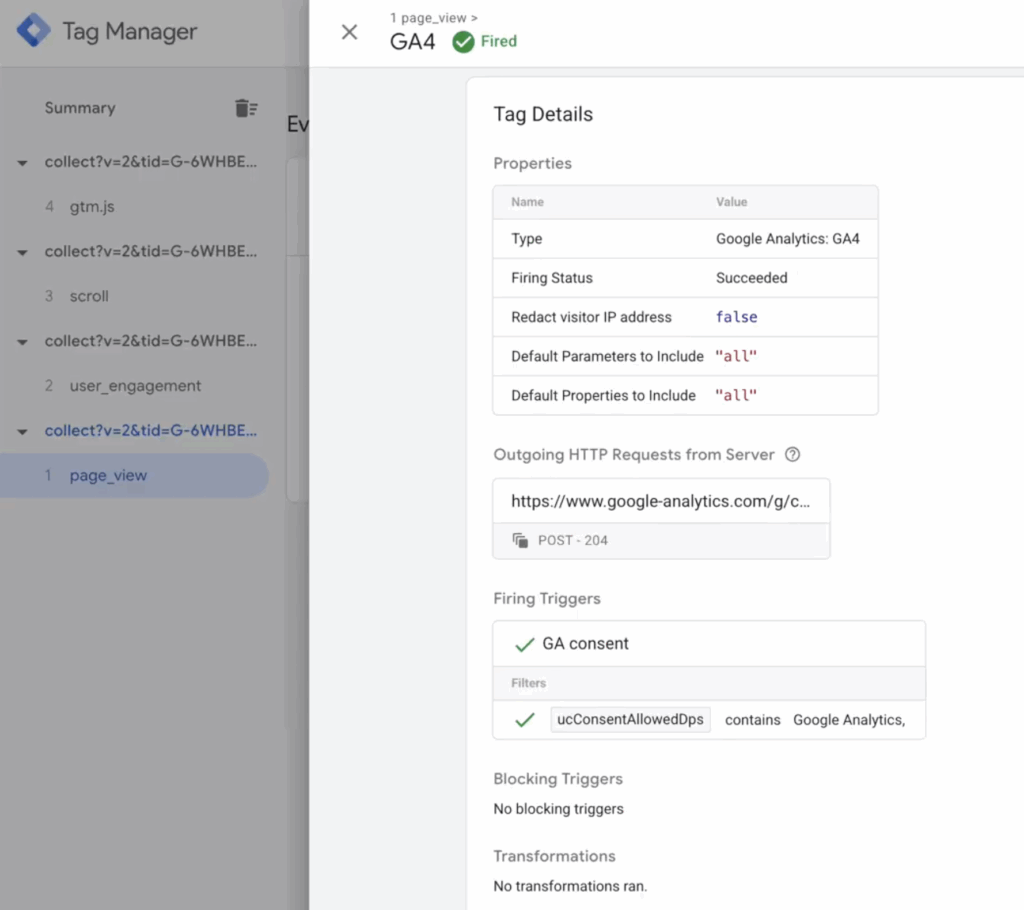
When done properly, server-side tagging provides a more controlled, privacy-friendly, and reliable way to collect analytics data — while reducing your reliance on client-side scripts.
Use cases for Google Analytics server-side tagging
Server-side tracking comes with plenty of advantages, but that doesn’t mean it’s the right solution for every business. It tends to deliver the most value in specific scenarios.
Here are some of the situations in which server-side tagging makes the most sense.
E-commerce tracking with enhanced security
Online retailers handle sensitive customer information throughout the purchase process. Server-side tracking enables you to collect detailed ecommerce data while maintaining strict security controls.
You can track product views, cart additions, and purchases without exposing sensitive data to client-side scripts. Payment information, customer details, and order data remain secure on your servers while providing rich analytics insights.
This approach is also valuable for businesses in regulated industries like healthcare or finance, where data security requirements are especially strict.
Ad campaign attribution without relying on third-party cookies
Third-party cookie restrictions make it difficult to attribute conversions to your advertising campaigns. Server-side tracking helps maintain attribution accuracy by using first-party data and server-side identifiers.
When a user clicks on your ad, you can store campaign parameters in your database and associate them with subsequent conversions through server-side events. This method provides more reliable attribution data than browser-based tracking alone.
Personalization with first-party data
Personalization engines need detailed behavioral data to deliver relevant experiences. Server-side tracking enables you to combine Google Analytics data with your customer database, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and other first-party sources.
This unified view supports more sophisticated personalization while helping to maintain privacy compliance. You can segment users based on their complete interaction history rather than just browser-based behavior.
Taking control with Google Analytics server-side tracking
Server-side tracking is more than a technical tweak; it’s a strategic shift in how you manage your analytics. By routing data through your own infrastructure, you gain more accurate reporting, stronger privacy compliance, and the ability to protect against data loss caused by ad blockers and browser restrictions.
Whether you’re running an e-commerce store, managing ad campaigns, or building personalized customer experiences, Google Analytics server-side tracking gives you the tools you need to stay ahead in a privacy-first world.
If you’re ready to take control of your data and future-proof your measurement strategy, server-side tagging is the next step.
