Consumers’ personal data is being collected, stored, and used online all the time. This is why personal privacy is a pressing issue for both consumers and businesses, especially as data privacy regulations become more prevalent. With the increasing growth of digital platforms and services, stricter requirements for data collection and use, and the widespread adoption of personalized marketing, companies are continuously seeking innovative ways to leverage data.
Thanks to data privacy legislation such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California’s Privacy Rights Act (CCPA), consumers now have more privacy rights and often a right to anonymity. This helps to ensure that when organizations use personal data in some cases — where they don’t need to know the user’s identity and consent does not need to be obtained — be used to identify any individual person.
This concept lies at the heart of data anonymization. There are other, similar functions that we will explore, like de-identification and pseudonymization, as well as their uses.
What is data anonymization?
In short, data anonymization is the process of protecting private or sensitive personal information by erasing or encrypting identifiers that connect an individual to stored data or make them identifiable using one or more pieces of that data.
It refers to the act of permanently stripping personally identifying information (PII) in such a way that an identification link can not be re-established. This means that this type of data is not subject to consent requirements because it does not identify individuals.
However, anonymized data can’t guarantee complete anonymity, and real-world cases have shown that at times anonymized data has been re-engineered to be identifiable again. This can be done for identity theft, fraud, or selling more complete data profiles. There is a particular risk when the anonymized data is combined with publicly available sources.
What is data de-identification?
De-identification refers to the removal of PII from datasets to protect individuals’ privacy. In other words, data processors should be able to handle the information, such as for analytics or research, without having any recognizable link to, or being able to directly identify, the person it came from.
It’s worth noting that de-identified data can be re-associated with the person it came from, so the information necessary to do this must be kept separate and secure to avoid privacy violations.
In addition, unlike some other similar functions, de-identified data is subject to consent requirements and must be included in your privacy policy and cookie banner.
What is pseudonymization
Pseudonymization is a form of data de-identification in which personal identities are replaced with artificial identifiers or pseudonyms. For example, stripping a real name and replacing it with “Jane Doe” is pseudonymization. However, in reality, it’s usually a random ID.
It’s not impossible to re-identify data that’s gone through any of these three procedures or to reverse engineer the process that was used to de-identify the data, so it’s not a guaranteed action. Organizations need to be careful about:
- how the removal of identifying factors is done
- how the resulting data is stored (including data that could be used for re-identification)
- what the de-identified data is used for
- how users are notified about the process being done
- what consent is obtained (if needed)
- what other data may be available that could contribute to re-identification (e.g. publicly available sources)
What is data de-anonymization?
Data de-anonymization is the opposite of data anonymization. Also known as data re-identification, it’s a technique used in data mining to re-identify encrypted or obscured information. This is done by cross-referencing anonymous data with other data sources to uncover the source of the anonymous data and reverse the anonymization process to reveal the identities of individuals associated with the data.
De-anonymizing data is not inherently illegal, but it may raise privacy concerns and potentially violate data protection regulations. The legality of de-anonymizing data depends on the context, the purpose of the de-anonymization, and the applicable laws and regulations. De-anonymizing data can be used for various legal purposes, such as research or marketing. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the de-anonymization process is conducted in a secure and responsible manner that respects individual privacy rights and complies with applicable laws and regulations.
Read about marketing data management now.
Data anonymization examples and use cases
Some sectors, such as market research companies, government organizations, and medical and research organizations often use data anonymization to safeguard confidential information while collecting data at a large scale. For example, hospitals and research labs often collaborate. Therefore, hospitals will implement data anonymization techniques to share valuable yet private information.
Another sector that often uses data anonymization is retail. Retail businesses rely on customer data for insights and market research. However, getting explicit consent from customers for this purpose can be challenging. Through data anonymization, personalized parts of the data can be obscured or entirely removed, thus enabling retailers to unlock more value in their data.
The financial sector also uses data anonymization to protect sensitive customer information, like bank account details, credit card numbers, and transaction histories. Doing so allows for data analysis, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance without compromising their customers’ privacy.
Lastly, the educational sector also benefits from data anonymization to protect their student’s privacy and detailed records.
Advantages of data anonymization
There are obvious benefits to adopting data anonymization. These include:
- Enhanced data security: Anonymizing data can significantly reduce the risks associated with data breaches by removing or hiding sensitive and/or easily identifying details of personal information, such as names, addresses, and social security numbers.
- Achieve regulatory compliance: Data anonymization can be a crucial practice for ensuring your company’s compliance with data protection regulations, depending on your purposes for data processing. By anonymizing data, you may be able to legally process personal data without risking privacy violations. It’s important to be familiar with relevant privacy regulations. You can still derive valuable insights from the data while respecting regulatory requirements and protecting individuals’ sensitive information.
- Improve trust and reputation with users: By anonymizing data and being clear with users about how and why it’s done, your organization shows it values privacy. This is one of a few ways to build trust.
- Improved security: By implementing data anonymization, you make the data less attractive to hackers or thieves, potentially discouraging attempts to access, steal, or sell it.
Disadvantages of data anonymization
Data anonymization, while potentially important for privacy protection and regulatory compliance, comes with certain drawbacks that your company should be aware of.
- Less accurate data: Using traditional data anonymization methods often means losing valuable information, which can make it hard to get useful insights for analysis and research. Balancing privacy and usefulness can limit the effectiveness of data-driven decision-making.
- Fewer marketing uses: Anonymization can limit the purposes for which the user data can be put to work, even with consent, e.g. it prevents the data from being useful for personalized marketing.
- Best for anonymized aggregate data: Data anonymization is useful for analyzing overall trends with grouped data. But when it comes to individual-level analysis, like in health research, anonymization can be a roadblock.
- Privacy risks remain: Even with data anonymization, there’s a risk of someone with malicious intent being able to re-identify individuals. As machine learning models get better, they can potentially re-identify anonymous data. So, anonymization doesn’t always mean complete privacy, and the tools to reverse anonymization are getting more powerful and accessible.
- Makes collaboration with third parties more difficult: Anonymized data can make collaboration with third parties harder because you can’t easily integrate data from different sources after anonymization, thus limiting its potential analytical value. Anonymization may make data of little use to some third parties that need data for sales and marketing purposes, especially if they specialize in targeted campaigns or data sale.
What data should be anonymized?
Not all datasets require anonymization, so marketers, database administrators, and others must determine which ones do, both for data processing purposes and requirements of relevant data privacy laws.
In practical terms, compliance standards and organizational policies both typically result in classifying certain PII as sensitive data that should be anonymized for certain uses. Certain types of data are typically recognized as PII, regardless of legal or industry definitions.
- name
- home address
- Social Security or similar government ID number
- IP address
- biometric information
- phone numbers
- credit card number
How data anonymization helps protect privacy?
Online data protection and privacy are growing concerns among consumers. Most people have no idea how many “digital crumbs” they leave online, and thinking about it could quickly become overwhelming. However, the onus of privacy and security should not be entirely on consumers, and data privacy laws help to focus the responsibility for data privacy compliance and protection of the data accessed onto those that collect it, like the companies whose websites we visit or apps we download.
Data anonymization helps protect online users by helping to prevent the exposure and exploitation of people’s sensitive information. When personal data is leaked, stolen, or illegally sold, the results can range from a minor annoyance to catastrophic, e.g. with identity theft or extortion.
By hiding PII data and rendering it anonymous, you’re not only working to comply with regulations like the GDPR and CCPA, but you’re making a visible effort to increase trust with users and customers.
How to anonymize data?
Today, most businesses online collect some form of personal data, and not just in e-commerce. There are several ways that personally identifiable information like names, credit card numbers, email addresses, etc. can be anonymized from their owners:
- Data masking: hiding data via altered values. Some common data masking techniques include word or character substitution and character shuffling. But this information can be re-identified so it’s not true anonymization.
- Generalization: deliberately removes some of the data to make it less identifiable. This technique eliminates sensitive parts of data without changing the important information. For example, removing some parts of home addresses while still keeping the general geographic location intact.
- Data swapping: also known as shuffling and permutation. As the name suggests, this method rearranges data so the same data points are in the dataset, just not in the original order.
- Data perturbation: this technique uses a proportional factor to add what data scientists call “random noise” to a dataset. This involves randomly altering some data points by random amounts. However, random noise can also be filtered out, so this method isn’t foolproof either.
- Synthetic data: is the only technique that may be acceptable under the GDPR and similar regulations. It involves creating artificial datasets that look like the original dataset and retain the same relevant properties. The GDPR doesn’t explicitly discuss synthetic data, but it states that the regulation applies only to data that has a link to “an identifiable natural person”, which synthetic data does not, even if it mimics real user information.
Data anonymization and the GDPR
The GDPR defines anonymous data as data that “does not relate to an identified or identifiable natural person or to personal data rendered anonymous” so “the data subject is not or no longer identifiable.” This means that if data has undergone anonymization techniques, such as encryption or removal of personally identifiable information, rendering the data subject no longer identifiable, the GDPR does not apply to that data.
However, the EU’s data anonymization policy is unclear. This can lead to challenges for organizations seeking GDPR compliance. The GDPR does cover anonymization in Recital 26, but there is a lack of clear guidance on what constitutes effective anonymization in practice.
A consent management platform (CMP) like Usercentrics Web CMP or Usercentrics App CMP can help your company with informing users and obtaining consent for the collection and use of personalized data. Even when the data will be anonymized, consent remains a requirement for several uses.
Data anonymization best practices
Data anonymization sounds like a solid tactic for protecting personal data and privacy, but there are some aspects that remain legally unclear, so it can be hard to know how to properly implement a successful data anonymization strategy. There are some best practices, however.
1. Understand your data: Before anonymizing (or even collecting) data, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the types of data you collect, how they’re stored, and how they’re used. This includes identifying what information is considered sensitive or personally identifiable, and how it may be connected to or used with other personal data.
2. Prioritize what needs to be anonymized: Not all data needs the same level of anonymization. Identify the specific use cases for your data and prioritize them accordingly. Also, some purposes require that data remain intact, e.g. personalized marketing efforts, so for some uses data cannot be anonymized so all other legal and security requirements for data collection, storage, and use must be observed.
3. Map out relevant legal requirements: Different regions and industries have specific regulations regarding data protection and use, which should include anonymization. Ensure compliance with laws such as the GDPR, CCPA/CPRA, and others where relevant. Align your anonymization practices with these legal standards to avoid potential fines and penalties.
4. Conduct data discovery and classification: Conduct a thorough data discovery process (e.g. as part of a data audit) to identify all direct and indirect identifiers within your dataset. This includes personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, addresses, and social security numbers, as well as indirect identifiers that could potentially lead to re-identification when combined.
By following these four best practices, your organization can anonymize data to protect privacy and security while still deriving valuable insights for analysis and research purposes.
The future of data anonymization
The escalating frequency of data breaches and the heightened scrutiny of privacy regulations underscore the critical need for businesses to prioritize data privacy.
Whether initiating new efforts or enhancing existing measures, the imperative lies with organizations that need user data to limit and safeguard customer information while ensuring transparency through easily accessible data privacy policies.
By proactively addressing these foundational steps, businesses can fortify their operations, build trust with customers, and navigate the evolving landscape of data protection with resilience and integrity.
Cookie banners, also known as “consent banners” are not new. In fact, they are quickly becoming an expected part of the user experience when visitors arrive on websites for the first time. This is because privacy laws are increasingly requiring companies to obtain visitors’ or customers’ consent before collecting, using, or selling their personal information.
These requirements are included in data privacy laws like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), ePrivacy Directive, California Consumer Protection Act (CCPA), and Brazilian Data Protection Law (LGPD). Clear, transparent compliance with them, including implementing a cookie banner on your website, for example, also helps build trust and encourages long-term relationship development with your users and customers.
What is a cookie banner?
Read about optimize cookie banners now
Since the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into effect in 2018, cookie banners are the new normal. When a user visits your website for the first time, a pop-up window or banner will appear. It’s intended to inform the user about the processing of their personal data.
A cookie is just a small text file, saved in the user’s browser, and used to store information. It enables functions like the web server’s ability to “recognize” a user on future visits to the site.
Cookies can be set in a browser without the user knowing it. However, the question is whether it’s legal to do so or not.
How does a cookie consent banner work?
Consent banners or cookie consent popups appear on or over a website’s homepage content and are interactive. Once users have selected consent preferences in the cookie banner – if they interact with it at all – those preferences are saved by your website’s Consent Management Platform (CMP).
A cookie banner gives your website visitors control over their website experience, how they are tracked, and how their data is used. It informs visitors about the web technologies, including cookies, used on the website to ensure its proper functioning.
Additionally, cookies can also track user behavior and collect data about them and their actions.
Given this information, cookie banners must provide options to enable or prevent the use of those technologies.
Benefits of a privacy-compliant cookie banner
Privacy violations come with hefty fines. However, the worst part is losing your customer’s trust and negative word of mouth.
Because people are becoming increasingly aware of privacy and rights regarding their data. Showing that you take their privacy seriously via a cookie consent popup empowers them to control access to their data and can be a key competitive advantage.
Additionally, consent management best practices increase user trust. This means that people are more inclined to share more of their data upon seeing a cookie consent banner since a company is being transparent about its collection and purposes of use. More data means better insights for marketing, as well as more ad revenue.
Cookie banner requirements
Cookie banners have to provide visitors with clear information in plain language about their:
- Privacy rights,
- About which web technologies, like cookies, are used on that site,
- For what purposes,
- A link to the company’s privacy policy should also be included.
Cookie banners have to provide users with consent options. So a website visitor must be able to opt in or opt out of the use of cookies entirely. Alternatively, they can customize which services they will allow to access their data.
Types of cookie consent banners
There are three primary types of cookie consent banners that can be integrated into a company’s website.
Notice-only cookie banner
This type of consent banner is usually located at the bottom of a page and informs people about the use of cookies being processed on a website. However, it does not give the option of a granular decision.
This is not a GDPR-compliant cookie banner. You can use notice-only cookie banners under the CPRA, but you’ll also need certain links on your homepage to be compliant
Implied consent (opt-out) cookie banner
This popup or banner assumes user consent based on actions such as continuous use of the website. For instance, a banner might state, “Continuing to use this website will be taken as consent to use cookies.” Therefore, people are typically required to take action if they want to reject the use of certain types of cookies.
Opt-out cookie banners align with data privacy laws like the CCPA, which don’t mandate explicit user consent for cookies. However, this is not a GDPR-compliant cookie banner.
Explicit consent (opt-in) cookie banner
Lastly, this category of consent banner requires people to actively agree, typically by clicking “Accept,” to permit the use of cookies and other tracking technologies placed on their device. This option offers clearer control and is a cookie banner example that can be fully GDPR compliant.
Companies can choose the most suitable type of cookie consent banner based on factors such as user experience, jurisdictional compliance, and the specific needs of the website.
Cookie banner design examples and best practices
Cookie consent banners come in various designs. However, there are certain best practices to follow when creating a cookie consent pop-up to ensure that it is transparent, clear, and provides people with granular control while being user-friendly.
For starters, your cookie banner text should inform the visitor about the cookies the website is using and their purpose. It should leave no confusion. This means you offer people the option to both “Accept” and “Reject” options. Once someone sets their cookie preferences, they should be able to modify them at any time via a prominent link or a button on the webpage.
Additionally, take the time to create a personalized consent banner that matches your brand’s visual identity. A cookie consent banner that fits in with your brand — in terms of colors, fonts, and language — feels more personal and intentional than one that hasn’t been customized at all.
How to install a cookie banner on my website?
There are multiple ways to install a cookie banner on your website. The first is to use a Consent Management Platform, such as Usercentrics, that enables you to create a customizable GDPR-compliant cookie banner in minutes. Our software will scan your website so you know which cookies and tracking technologies are collecting data. Then, we’ll help you comply with global privacy laws by recording and maintaining a log of the cookie consent you receive from website visitors.
Another option is to manually code a cookie banner for your website. Add a short explanation as to the purpose of cookies, a clear statement on which action will signify consent, as well as a link to a cookie policy. However, under EU law, if your website uses any non-exempt cookies or scripts, these scripts must be prevented from running until a website visitor explicitly grants consent.
Read about cookie policy now
Therefore, a CMP is an easier option to implement as it requires less effort to set up and is more likely to help you remain compliant with privacy laws while automating the cookie consent management process.
Read about eCommerce consent requirements now
Is a cookie banner mandatory?
While data privacy laws are passed in specific regions or countries, your website visitors and customers can come from pretty much anywhere in the world. So the type of cookie banner you need to comply with privacy law typically depends on where your visitors are located, not your company.
So the answer to “Do I need a cookie banner on my website?” is “Most likely you do, yes” and “Why would you risk not having one?” Especially given that, in addition to not wanting to risk violations and fines, you don’t want to jeopardize the trust of your users and customers.
Legally, cookie banners have to provide all of a user’s cookie usage consent options and the ability to exercise them equally. They cannot use text or graphics (or the absence of them) to manipulate users into the “consent” that the company wants.
However, not all privacy laws are the same. For example, the EU’s GDPR and Brazil’s LGPD use an opt-in model, where user consent must be obtained before data can be collected (or used).
However, under US laws like the CCPA, an opt-out model is used. So companies only have to obtain users’ consent before personal information is sold. Consent is not required before or when such data is collected.
There are also or will be more specific considerations for minors and data classified as “sensitive personal information”, especially under the successor to the CCPA, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA).
GDPR-compliant cookie banner requirements and best practices
GDPR doesn’t explicitly mention cookies, but it does have several requirements for consenting to data processing and collection. According to Art. 4 of GDPR, user consent must be:
- Freely given
- Informed
- Specific
- Unambiguous
- Revokable
- Obtained before any data is collected
So to create a GDPR-compliant cookie banner, appearance, content, and functionality must meet the above requirements. You cannot coerce or manipulate the user into giving consent, consent must be freely given. And you must clearly describe what kind of data your website will collect upon consent and what the implications of giving consent are.
A GDPR-compliant consent banner requires the following:
- Cookie banners or pop-ups should indicate the use of cookies and other trackers on your website.
- The cookie banner must ensure that the user can give their consent.
- Users have the option to give a granular consent for different processing purposes.
- People must be presented with an opt-out option, which can be through a widget or a link.
- Includes a link to your full privacy policy, cookie policy, and cookie settings.
- Documents a user’s choice in the event of a review.
-
Cookie banner best practices to comply with CCPA and CPRA
To comply with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), your cookie banner should focus on providing a notice of collection. Inform users about your website’s data collection practices, including the use of cookies. This is according to CPRA Section 1798.135.
Unlike GDPR, the CCPA and CPRA do not require businesses to obtain cookie consent. Instead, it emphasizes the importance of providing a clear notice of data collection to users. This means that your cookie banner should be designed to serve as a notice of collection, providing easy-to-read and understandable information about the categories of personal information collected, and the purposes of such collection.
In addition, companies also need to include the links mentioned above somewhere on their website homepage, usually in the footer.
Are there fines for non-compliant cookie banners?
Cookie banners are no longer just a formality, they are a necessity. And if your consent banner does not comply with local regulations, you’ll face hefty fines.
For example, under the GDPR, Art. 84, fines can be up to €20 million EUR or 4% of a company’s global annual revenue, whichever is higher. In the US, the CCPA and CPRA can impose fines of up to $7,500 USD per violation. In the UK, the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) can impose fines of up to £17.5 million GBP or 4% of a company’s global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
Fines can be imposed for various reasons, such as not obtaining proper consent, not providing clear information about data collection and use, or not giving users a genuine choice to accept or reject cookies.
Therefore, your cookie banner must be compliant with relevant local privacy laws to avoid potential fines.
Do all types of cookies require user consent?
Cookies are not the only web technology that can be used in a browser for tracking or data collection purposes. Tracking and retargeting pixels are also used. Regulations like GDPR, include all such technologies that process personal data in any way.
“Strictly necessary” cookies enable a website to function as intended and do not require user consent to be loaded. For example, if you want your customers to be able to browse your e-commerce website while saving the items in their shopping cart, that requires cookies. And for this, you do not need consent. However, other types of cookies do require consent.
Analytics cookies, which provide details like how many visitors are on the website and what pages or functions they’re accessing, do require user consent. As do third-party cookies that track users when they go to other websites or any web technologies that collect users’ personal information, such as name, IP address, location, or other data that can be used to identify a person.
A website should only load the cookies that a user has consented to. However, there are tools, like Google Consent Mode, that help recover valuable data and provide analytic modeling even without the data processing that’s enabled by user consent.
To achieve full privacy compliance on a website, a simple cookie banner is not enough to meet GDPR requirements. And other international privacy laws, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), have specific requirements as well. Therefore, using a cookie banner correctly is just one part of a solid data privacy strategy for your website.
A Consent Management Platform will help you check off all necessary privacy compliance requirements, no matter what your website is used for, and even if you’re subject to multiple countries’ data privacy laws.
How a Consent Management Platform (CMP) can help
A Consent Management Platform (CMP), such as Usercentrics, offers all the necessary features to ensure you can create, design, and publish a privacy-compliant cookie banner. Specific relevant laws and web technologies used on your site, customize the appearance of your banner, and clearly communicate with your website visitors to maintain an accessible and transparent privacy policy for everyone.
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) is the state’s second data privacy law, which came into effect in 2023. It amends and expands on the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which came into effect in 2020. While the CCPA was the first state-level data privacy law in the United States, 12 other states have followed suit since with comprehensive data privacy laws. (Florida has also passed a privacy law, but it is much narrower in scope than the other state-level privacy laws, and Nevada also has some narrower and older regulations.)
There has been significant evolution in the data privacy and technology landscapes since 2020, and even in the 15 months between when the CPRA came into effect and when enforcement by the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) commences. The CCPA coming into effect saw a number of class-action lawsuits and other responses, which are likely to be influential over time on updates to the regulations, enforcement, and case law.
We look at the key changes that have come with the CPRA, the requirements to comply — including if you’ve already pursued CCPA compliance — the authorities overseeing enforcement, and how organizations can best be prepared and protect their operations and users’ personal data.
Who needs to comply with the CPRA?
Like the CCPA, the CPRA is extraterritorial, so it protects California residents and applies to any qualifying organization processing their personal data, even if the company is not located in California.
The qualifying thresholds for organizations changed from those set out in the CCPA, and under the CPRA companies meeting the following criteria must comply with the law:
- annual gross revenues exceeding USD 26,625,000 in the preceding calendar year
or
- receiving, buying, or selling personal information of 100,000 or more consumers or households
or
- earns more than 50 percent of their annual revenue from the sharing or sale of consumers’ personal information
Check your website privacy compliance for CPRA requirements. Get your free data privacy audit now
What are the restrictions to data processing under the CPRA?
Under the CCPA there were already controls and restrictions on the sale of personal data. The CPRA adds the sharing of personal data to those rules. This means that in many cases users must be given the option to opt out of both sharing and sale of their personal data. The restrictions apply to sensitive personal data and also to data belonging to minors in order to comply with the CPRA.
There are also restrictions on how personal data can be used for targeted or behavior-based advertising, and profiling used to create such campaigns. Consumers must be able to opt out of this use in most cases in order to comply with the CPRA.
How are third-party data processing arrangements affected by CPRA enforcement?
More restrictions on data processing have been introduced with the CPRA, including the access third parties have to it. Any third parties undertaking data processing on behalf of a data controller or otherwise providing services wherein the data can be accessed must have contractual agreements in place before the data processing begins.
The contracts have to cover the new restrictions on disclosure, sharing, sale, purposes for these actions, and exercising of consumers’ rights (like deletion requests or processing opt-outs).
Consulting with qualified legal counsel and/or a privacy expert is strongly recommended when setting up new contracts or reviewing/updating existing ones that may have been put in place for CCPA compliance.
What rights do consumers have under the CPRA?
Consumers’ rights have been expanded under the CPRA, so there will be more restrictions on data processing to be enforced. The user consent standards that require it to be “freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous indication of the consumer’s wishes” remain in place. Additionally, use of dark patterns to obtain user consent is specifically referenced and prohibited by the CPRA.
Consumers’ privacy rights under the CCPA
- Right of access:
- to know whether their personal data, or that of their children, is being collected and processed, and which data it is
- to know if their personal data is being sold to other individuals or companies
- to view the personal data collected about them at any time
- Right to opt out of the sale of their personal data
- Right to deletion of personal data collected from them (with some exceptions)
- Right to non-discrimination for exercising their CCPA rights
Additional consumers’ privacy rights under the CPRA
- Right to correction of inaccurate or incomplete data collected about them
- Right to data portability to receive a copy of their personal data they can take with them from one business, platform, etc. to another
- Right to restrict sensitive personal data, limiting its collection and use, including that of children
- Right to access information about automated decision-making, to request information about automated decision-making (e.g. AI tools) and likely outcomes of using such processes, particularly with regards to profiling
- Right to opt-out of the use of automated decision-making technology with regards to their personal data
Modifications of existing consumers’ rights granted under the CPRA
Consumers can request their personal data that was collected before the CPRA’s look-back period (the 12 months prior to January 1st, 2023) as long as it’s possible or not unreasonably difficult to provide.
In addition to opting out of the sale of their personal data, consumers can now also opt out of the sharing of it with third parties.
The right to have personal data deleted includes both the company that collected it and any third parties that received, processed, or purchased it (with some exceptions).
Minors’ personal data cannot be shared or sold without explicit consent (from a parent or guardian), and if consent is declined, it cannot be requested again for 12 months.
Under the CPRA, “browsewrap agreements” are no longer allowed. This is when a website has its terms and conditions listed somewhere, potentially not prominently, and the terms state that you agree to them simply by using the website. This violates the requirement that consent be explicit and specific.
Data controllers also need to be able to prove consent, so in addition to being obtained, it must be securely stored and accessible in case of an audit or data access request.
What are the penalties for violating the CPRA?
Both the CCPA and CPRA require organizations to ensure that they have robust security processes in place to protect personal data and processing operations. Data controllers are also ultimately responsible for the activities (and any violations) of third-party processors under contract to them.
The “reasonableness” of security efforts depends on the volume and types of data processed, so the greater the volume and/or the sensitivity of it, the more robust the security of staff, contractors, technology, and policies must be.
Fines for negligence violations
If the violation is negligence — failure to take reasonable steps to achieve compliance — a company can be fined USD 2,663 per violation.
Fines for willful violations
Fines for a willful violation — the company intentionally did something that violated the law — can be up to USD 7,988 per violation.
Fines for violations involving minor
Fines for violations involving minors under the age of 16 have been increased to USD 7,988 per violation (from USD 2,663) under the CPRA.
Consumer rights and compensation for data breaches
Affected consumers are entitled to damages ranging from USD 107 to USD 799 per person for a data breach. California is also the only state among those in the US with data privacy laws that enables private right of action, where consumers can sue companies for violations that affect them. That right was introduced with the CCPA.
The CPRA eliminated the 30-day cure period that companies could receive under the CCPA to correct noncompliance issues without penalty.
CPPA enforcement action against American Honda Motor Co.
In March 2025, the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) Board issued a decision against Honda. The Enforcement Division of the CPPA alleged that Honda violated the privacy rights of California residents with the following actions:
- Californians were required to verify themselves and provide excessive personal information in order to exercise their privacy rights under the CCPA/CPRA, including the right to opt out of sale or sharing of their personal information and the right to limit processing of their data.
- The online privacy management tool Honda used did not provide equal privacy options.
- It was difficult for Californians to appoint an authorized agent (another individual or organization) to exercise their privacy rights for them.
- Consumers’ personal information was shared with ad tech companies without consent or contracts with the necessary terms for privacy protection.
To resolve the issues, Honda has agreed to change their privacy management processes, making it easier and simpler for Californians to exercise their rights. The company must also:
- Consult a UX designer to evaluate its process for consumers to submit privacy requests
- Change its process for contracting to ensure adequate protection mechanisms are in place for personal information
- Train its employees
- Certify its privacy compliance
Honda will also pay a fine of USD 632,500. This amount is based on the number of consumers whose rights were potentially violated by Honda’s practices. The CPPA is authorized to impose administrative fines of up to USD 2,663 per violation or USD 7,988 per intentional violation (USD 2,500 or USD 7,500 adjusted for inflation).
Who is responsible for enforcing the CPRA?
The California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA) was introduced with the CPRA, and is governed by a five-member board with a Chief Privacy Auditor.
Legal challenges and CPRA enforcement delays
The Agency came into effect with the law in January 2023, and enforcement was scheduled to begin July 1, 2023. However, this was delayed by a legal challenge, and later the start date for enforcement was changed to March 29, 2024. That changed again in February 2024 when an appeals court sided with the CPPA, clearing the way for CPRA enforcement to begin immediately.
Differences between the CPPA and Attorney General’s office and enforcement responsibilities
Under the CCPA, administration and enforcement was handled by the California Attorney General’s office, though the CPPA has greater influence, jurisdiction, and obligations.
In addition to handling complaints, investigations, audits, and levying fines or other penalties, the CPPA takes over the interpretation of the CCPA/CPRA, which will have long-term influence over establishing how compliance is monitored, violations are punished, and fines are doled out. Its actions will also affect class-action lawsuits that come about as a result of alleged violations.
Mandatory risk assessments and cybersecurity audits for high risk activities are requirements introduced with the CPRA, and those risk assessments have to be submitted to the CPPA.
The CPPA monitors the data privacy landscape around the US and globally, as well as evolving technologies and their applications. This enables it to provide advice and technical assistance to the California state legislature and other jurisdictions. This will also influence updates to California’s privacy laws, or the drafting of future ones.
US data privacy regulations explained: Watch our on-demand webinar
What you need to do for CPRA enforcement
Organizations that have already done the work of CCPA compliance won’t need to do a great deal more for CPRA compliance. However, there are changes and new restrictions, so it’s important to review the following and update where needed:
- requirements and changes that come with the CCPA and CPRA
- your company’s data processing activities, including a data audit
- your company’s security measures, including staff training and data access
- contracts with any third parties that do data processing for you
- contracts with any other service providers with whom data is shared
Review your privacy policies and legal notices
Legally-mandated notifications for consumers, such as the content of privacy policies, will need to be updated, and clearly visible opt-out notices for sale or sharing of personal data will need to be present and updated.
You must provide information about what data is processed, for what purposes, who may have access to it, and how long it will be retained. Additionally, consumers must be notified about their rights, how to exercise them, and provided with a mechanism, such as a phone number or web form, to do so.
Implement a consent management platform to ensure your websites and apps are compliant
A consent management platform (CMP) like Usercentrics CMP for web or apps can help ensure that the right information and choices are provided to the right users at the right time. With geolocation functionality, it can also help ensure that you display the right regulatory information to different users around the world, if you do business outside California.
Prepare to swiftly handle data subject access requests (DSAR)
Users can request access to their data, as well as changes to it or deletion of it. Ensure that you have a robust and efficient system to handle data subject access requests. The CPRA does require they be handled within a specific time frame, typically 45 days unless there are legitimate extenuating circumstances.
Stay up to date with US privacy and regulatory developments
Data privacy regulation and digital technologies are evolving at an ever-increasing pace, so it’s also important for organizations that process users’ personal data to keep up with what is happening in legislation, with changes to technology, and with consumers’ increasing savvy and concerns about privacy.
We recommend subscribing to the Usercentrics newsletter to get all the latest news from the data privacy landscape, exclusive invitations to our events, and more delivered monthly right to your inbox.
Usercentrics does not provide legal advice, and information is provided for educational purposes only. We always recommend engaging qualified legal counsel or privacy specialists regarding data privacy and protection issues and operations.
As consumers become more data privacy-aware, Google is taking proactive steps to ensure that the privacy compliance requirements placed on them and other large tech companies by new regulations are also met by their third-party business customers. This helps ensure privacy compliance in the full digital ecosystem. As part of these enforcement efforts, Google has introduced strict requirements for verifiable user consent, particularly to enable continued access to Google ad personalization features. With a direct potential risk to companies’ bottom line, this move and other new requirements by Google could have a more significant impact on data privacy enforcement — and more quickly — than some government regulations and their enforcement by data protection authorities.
Shirin Eghtesadi, Google’s Director of Product Management, underscored the importance of these new measures:
“Google’s EU User Consent Policy (EU UCP) reflects the requirements of two European privacy regulations, the ePrivacy Directive (ePD) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and requires marketers advertising with Google to obtain and respect end-users’ consent. Starting this year, we will enhance enforcement of the EU UCP for audience and measurement solutions.”
Google has also implemented a range of tools and features to help advertisers comply with their consent policy requirements and government regulations while still reaching their marketing goals. This guide delves into the essentials for obtaining and signaling consent for Google ads personalization and how to achieve and maintain compliance with Google Ads requirements in Europe.
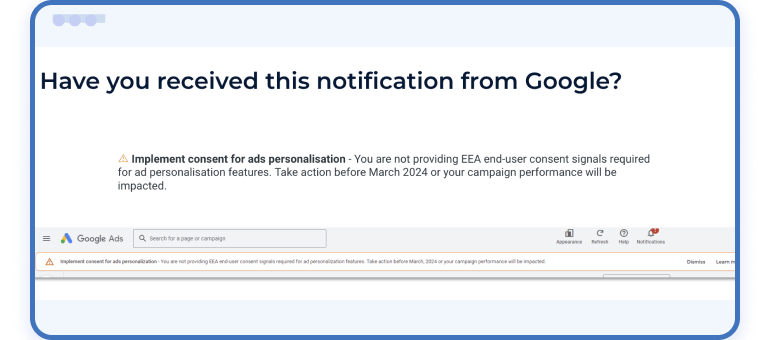
Understanding Google’s alert and requirements for consent in advertising
“Implement consent for Google ads personalization – You are not providing EEA end-user consent signals required for ad personalization features. Take action before March 2024 or your campaign performance will be impacted.”
This prompt in your Google Ads dashboard isn’t just a suggestion. It’s a critical update that represents a fundamental shift in how advertisers must manage user data.
Google’s introduction of the consent requirement is not arbitrary. It’s a strategic response to the global call for data protection, with regions like the EU/EEA and the UK setting stringent privacy standards with the regulations they pass.
Why has Google introduced this requirement? Adapting to the privacy-centric trend
Google has introduced the new requirements to their ad tech customers to align with an evolving regulatory landscape that prioritizes user privacy. With the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the ePrivacy Directive, there is a clear mandate for companies to ensure that personal data is processed lawfully, transparently, and for a specific purpose. Google’s consent requirements in ad tech and measurement tools aim to help advertisers meet these legal obligations and maintain trust with their users.
According to Google, these changes are part of their ongoing commitment to give users more transparency and control over their data, while providing advertisers with the tools they need to be privacy-compliant.
In short: If you saw the Google alert, you’re likely running ad campaigns on Google ad tech platforms or using Google Analytics to measure your ad revenue impact in Europe, but aren’t yet complying with all the recent requirements. Taking action to comply will ensure uninterrupted ad revenue after March 2024, when enforcement starts.
Learn why a Google-certified CMP like Usercentrics is essential for serving ads in the EU and EEA.
The regulations behind Google’s EU user consent policy and their implications for digital marketing
The GDPR and ePrivacy Directive are the primary regulation and directive informing Google’s EU user consent policy, together with the Digital Markets Act (DMA). The GDPR, in particular, affects any business that processes the personal data of EU residents, in many cases requiring explicit user consent for data processing activities. These laws have significant implications for digital marketing, where personal data is critical for targeting and personalization.
With the GDPR, the data privacy framework has shifted to empower users and place greater responsibility on advertisers.
Consent as a prerequisite
The GDPR has several legal bases for the lawful processing of personal data, but for digital marketing purposes, the most commonly needed one — user consent — mandates that it be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. For advertisers, this means deploying clear consent mechanisms that are easy for users to understand and act upon before any personal data is collected or processed.
User rights front and center
The GDPR stipulates that users have the right to access their personal data, or have it corrected or deleted. Additionally, if a user rescinds consent for data processing, advertisers must cease collecting and processing it immediately. Therefore, advertisers must implement processes that enable users to learn about and exercise these rights easily, without obstruction.
Data minimization as a strategy
The principle of data minimization — collecting only the personal data that is necessary for stated purposes — compels advertisers to refine their data strategies, focusing on quality over quantity. This leads to more targeted, efficient, and effective advertising efforts.
Consent for Google ads personalization: Assessing the impact on ad campaigns
The implementation of consent for ads personalization can result in reduced visibility into user behavior, and, consequently, less data for optimizing campaigns. Advertisers might observe a decrease in the size of remarketing lists and a reduced ability to measure the performance of ads accurately.
The requirement for user consent can lead to a paradigm shift in campaign strategy and execution:
- Targeting challenges: limiting the use of detailed personal data for ad targeting without explicit consent may decrease the precision and relevance of ads, which can impact campaign performance metrics.
- Performance metrics fluctuations: as users exercise their right to opt out of data sharing, advertisers may witness changes in key performance metrics. This underscores the importance of adapting campaign strategies to remain effective under the new consent-based framework. Google suggests that advertisers should be prepared for these changes and understand that users’ consent choices will directly impact the data available for ad personalization and measurement.
How to adapt advertising strategy: Comply with Google’s EU user consent policy
To comply with Google’s EU user consent policy, advertisers should ensure that they have a viable and provable legal basis for collecting, sharing, and using personal data. In most cases, this will need to be valid user consent. Advertisers must provide clear information about their data use practices and obtain affirmative consent from users in the EEA/EA.
Google provides Consent Mode, which helps advertisers manage how Google tags behave based on user consent. Advertisers are encouraged to use this feature to maintain privacy compliance while still collecting valuable data where consent is given. Google’s tools also help to fill in gaps with modeling to provide data for insights even when users decline consent.
Read about consent mode GA4 now
Compliance with Google’s EU user consent policy: Risks and opportunities
Noncompliance with Google’s EU user consent policy carries risks, including potential loss of revenue and access to Google’s platforms, as well as a loss of user trust. However, there are also opportunities to build stronger relationships with users through transparent practices and to innovate in targeting and measurement with privacy in mind.
User’s personal data that is collected with proper consent will be processed according to the user’s choices, helping to ensure privacy compliance while enabling advertisers to personalize and measure ad performance for those who have consented.
Impact of not using Consent Mode in Google Ads before March 2024
Failing to activate Consent Mode before March 2024 if you run ad campaigns targeting users in the EU/EEA or UK, you will see the following consequences in your Google Ads account.
1. Remarketing audience limitations
Population of remarketing audiences will cease. There will not be an abrupt halt to all remarketing campaigns by March 2024, but the audience list will gradually diminish in size until it becomes ineligible due to size reductions.
2. Discontinuation of feed-based dynamic remarketing
The feasibility of implementing feed-based dynamic remarketing will be compromised. This feature is especially effective for running shopping campaigns and retargeting users based on the shopping products they have previously viewed.
3. Inoperability of New Customer Acquisitions (NCA) bidding
New Customer Acquisitions (NCA) bidding will cease to function when the remarketing list dwindles below 1,000 active members.
4. Inability to create lookalike audiences for Demand Gen
Crafting lookalike audiences for Demand Gen will no longer be feasible. Given that this capability is integral to this campaign type, it’s advisable to implement Google Consent Mode.
5. Limitations in customizing audiences and loss of audience insights data
Customizing audiences based on parameters such as “recent users 30 days” will no longer be possible. Additionally, valuable audience insights data will be lost.
Constructing a GDPR-compliant framework
Compliance with the GDPR and Google’s requirements for advertisers can be a strategic opportunity to reinforce trust and improve the quality of interactions with your audience. A robust GDPR compliance framework encompasses several critical elements:
- Comprehensive consent management: Implementing a Google-certified consent management platform (CMP) from a Google CMP Partner like Usercentrics is essential for managing and documenting user consents in a transparent and verifiable manner, and a requirement that Google has announced.
- Transparency as a trust builder: Clear communication about data practices not only satisfies GDPR requirements, but also builds user trust. Users are more likely to provide consent when they understand how their data will be used and see the value in providing it.
- Empowering user autonomy: User control over data is a key tenet of the GDPR. Advertisers must ensure that users can easily manage their consent preferences, thereby respecting their privacy and autonomy.
Preserving data and conversion integrity amidst changing consent requirements
The potential loss of data following the implementation of consent mechanisms is a critical concern for advertisers, but with the right strategies, this challenge can be mitigated.
To maintain data quality and limit the impact on conversions, advertisers can employ several proactive approaches:
- Anonymization and aggregation: Collecting data in aggregate or anonymizing user data allows advertisers to continue to gather useful insights without infringing on privacy.
- Advanced Consent Mode implementation: Google’s Advanced Consent Mode is a flexible solution that adjusts tracking and data collection based on user consent. It enables advertisers to retain a level of data collection and tracking for users who give consent while respecting the choices of those who do not.
Read about Google additional consent now
Addressing consent for personalization
Meeting the consent requirement for Google ads personalization involves a multifaceted approach that marries compliance with effective marketing.
To navigate the consent landscape successfully, advertisers should consider a multi-step strategy.
Choose a Google-certified CMP
If you’re using Google Ads and/or Google Analytics or Google Marketing Platform for serving personalized ads in the EU/EEA and UK, you need to review the way you obtain and signal consent from end users. A Google-certified CMP like Usercentrics CMP for web and mobile apps can help you obtain and manage valid user consent, and it integrates seamlessly with Google Ads.
Implement the latest version of Google Consent Mode
In November 2023, Google announced an update to Google Consent Mode. Advertisers must ensure that Google advertising products are properly configured to respond to consent signals from users, obtained via a consent management platform, enabling continued data collection in a compliant manner.
Educating users
Providing users with clear notifications about data sharing and compelling information about its value can improve consent rates and help ensure a positive user experience.
How to minimize the impact of potential data loss from CMP implementation and maximize conversions
To minimize the potential impact of losing data from Consent Management Platform (CMP) implementation, Google advises adopting privacy-safe methodologies for measurement, like conversion modeling, which uses machine learning to estimate conversions.
Advertisers should also leverage first-party data, contextual targeting, and privacy-centric machine learning models. By focusing on these areas, they can maximize conversions while respecting user privacy and compliance requirements.
Optimizing data collection with Google Consent Mode
Google’s updates to Consent Mode offer advertisers a sophisticated tool to navigate the new consent requirements without losing valuable data.
Consent Mode enables adaptive strategies for data collection that respect user consent.
- Dynamic data collection adjustment: Google’s tags can dynamically adjust their operation based on the user consent provided, ensuring that advertisers can maximize data collection within the boundaries of user preferences.
- Innovative conversion modeling techniques: For users who do not consent to full tracking, Consent Mode employs statistical methods to estimate conversions, enabling advertisers to maintain insights into campaign performance.
Adapting to data reduction after consent banner implementation
While consent banners may result in reduced data collection, there are strategies to mitigate this impact and continue to derive valuable insights from your campaigns.
Adapting to the reduction in data requires a proactive and informed approach.
1. Adopting privacy-first technologies
Usercentrics’ server-side tracking and other privacy-first technologies enable advertisers to collect and use data in a responsible and compliant manner.
2. Promoting informed consent
Transparent communication about the benefits of data sharing can lead to higher consent rates. Users are more likely to share their data when they understand the value proposition and personal benefits.
3. Designing effective consent interfaces
A well-designed consent experience with a focus on user interface and user experience best practices can significantly improve user interactions and potentially increase the rate of consent, thus preserving the flow of valuable user data.
Advanced data collection with Usercentrics
Usercentrics provides a suite of consent and preference management solutions that enhance privacy while enabling effective data collection.
- Prioritizing user privacy: Usercentrics’ technology is built with privacy as a core value, helping ensure that advertisers can collect data in a manner that respects user rights and complies with regulations.
- Server-side tracking: Usercentrics’ server-side tracking reduces the reliance on third-party cookies and provides a more secure and privacy-compliant way to gather user data.
- Universal consent: Collect, centralize, and activate zero-party user data, consent and preferences, giving your website and app users full control over their marketing permissions to deliver truly personalized brand experiences.
Embracing privacy-centric tools for ad measurement
Google offers a range of tools designed to help advertisers measure campaign performance while navigating the evolving privacy landscape and the gradual phasing out of third-party cookies.
Advertisers can use these tools to maintain campaign effectiveness in a privacy-first environment.
Advanced conversion modeling
Google Consent Mode’s conversion modeling provides advertisers with estimated conversion data, helping to compensate for any decrease in full tracking data from users who decline consent.
Improved measurement capabilities
Enhanced measurement accuracy enables a deeper understanding of campaign performance, enabling better decision-making and optimization efforts.
Adopting new tracking paradigms
As the advertising industry moves away from reliance on third-party cookies, adopting new tracking technologies such as server-side tagging helps advertisers stay competitive and privacy-compliant.
Introduction to the India Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act)
India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Bill was tabled in 2022, and was finalized as India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act) when it received approval from both houses of Parliament and the assent of the President in August 2023. The law came into effect August 11, 2023 and covers personal data collected in digital format, or collected by other means and later digitized. The law is intended to protect personal information for citizens in the world’s most populous country, and increase accountability for organizations that handle a lot of such data, including those with online operations and that run mobile apps.
The law is in line with the standards of many global data privacy regulations, taking influence from China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). We look at important requirements of the DPDP Act, key definitions, enforcement, and more. (Note: the state-level Delaware Personal Data Privacy Act in the United States also uses the initialism “DPDPA”, so we will mostly use “the DPDP Act”.)
What is the India Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act)?
The DPDP Act is a federal law in India that regulates the processing of the digital personal data of its citizens. The law aims to strike a balance between the recognized need to process personal data for various purposes, and individuals’ right to control and protect it.
Like many data privacy laws around the world, the DPDP Act is extraterritorial, and so applies to organizations operating both inside and outside of India, if they are offering goods or services to Indian citizens, and in doing so processing personal data. The Act does allow for legal bases for data processing in addition to consent of the data principal, but consent is required for many processing purposes.
Key definitions in the Indian Personal Data Privacy Law
The definitions of key terms outlined in the DPDP Act are consistent with many data privacy laws, though some of the terms are different, e.g. “data fiduciary” instead of “data controller”. The definition of a person is also quite broad, as it can include the Indian State, a family, or a firm, for example.
What is a person under the DPDP Act?
A person covers a variety of entities, not just individual people, and refers to:
- an individual
- a Hindu undivided family
- a company
- a firm
- an association of persons or a body of individuals, whether incorporated or not
- the State
- every artificial juristic person, not falling within any of the preceding sub-clauses
What is personal data under the DPDP Act?
Personal data refers to any data about an individual who is identifiable by or in relation to such data. The personal data can be collected and processed in digital format, or collected in another format and later digitized. The Act does not provide a list of examples of personal data (e.g. name, phone number, financial information, etc.) like some data privacy laws do.
What is processing under the DPDP Act?
Processing in the context of personal data means “a wholly or partly automated operation or set of operations performed on digital personal data, and includes operations such as collection, recording, organisation, structuring, storage, adaptation, retrieval, use, alignment or combination, indexing, sharing, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, restriction, erasure or destruction”.
What is the definition of consent under the DPDP Act?
A data principal’s consent must be: “free, specific, informed, unconditional and unambiguous with a clear affirmative action, and shall signify an agreement to the processing of her personal data for the specified purpose and be limited to such personal data as is necessary for such specified purpose”.
Who is defined as a child under the DPDP Act?
A child is defined as a person who is 18 years old or younger.
Who is a data principal under the DPDP Act?
This term refers to any individual to whom personal data being processed relates, and includes an individual who is a child (also, then, including the child’s parents or lawful guardians) or an individual who has a disability (also, then, including the person’s lawful guardian, acting on their behalf). Also known as a data subject under some other laws.
Who is a data fiduciary under the DPDP Act?
“Data fiduciary” means any person who, alone or in conjunction with other persons, determines the purpose and means of processing of personal data. Also known as a data controller under some other laws.
A “Significant Data Fiduciary” refers to any data fiduciary or class of data fiduciaries as may be notified by the Central Government.
Who is a data processor under the DPDP Act?
A data processor is any person who processes personal data on behalf of a data fiduciary.
What is a consent manager under the DPDP Act?
For the purposes of the Act, “Consent Manager” does not refer to software such as a consent management platform, but instead refers to a person or organization registered with the Data Protection Board. This entity acts as the point of contact to enable an individual, here the “data principal”, to provide, manage, review, and/or withdraw her consent via a platform that is “accessible, transparent and interoperable”. A consent manager serves as a middleman for businesses to help facilitate compliance with the DPDP Act.
Who has to comply with the Indian data privacy law?
The law applies to entities that collect and process digital personal data in India in the course of offering goods and services. It also applies to the processing of personal data outside of India if the processing is connected with an activity relating to offering goods or services to Indian citizens.
What are consumers’ rights under the India DPDPA?
Data principals have some of the rights common under other global data privacy laws, but not all of them. These include:
- Right of access – to obtain information from the data fiduciary about their personal data, the processing of it, and identities of any third-party data fiduciaries or data processors with which it has been shared
- Right to correction – to get errors or omissions corrected or personal data updated as quickly as is reasonable (with some exceptions)
- Right to erasure – to have personal data deleted as quickly as is reasonable, including data held by and/or processed by a third-party data processor, upon request (with some exceptions)
- Right of grievance redressal – to have a readily available means to report a grievance, provided by the data fiduciary or consent manager, and have the grievance responded to within a reasonable amount of time from the date of receipt (with some exceptions)
- Right to nominate an agent – to have someone represent the data principal to exercise their rights under the Act on their behalf in the event of death or incapacitation
It should be noted that the right to erasure is not a full “right to be forgotten” as under the GDPR. Additionally, data principals do not have the right to data portability, to opt out of automated decision-making, or private right of action — the ability to sue a data fiduciary in the event of a breach — though they may seek compensation for a breach from responsible parties, and the Act does provide a schedule of penalties for different types and degrees of violation or negligence.
What are consumers’ responsibilities under the DPDP Act?
Data principals have several duties under the DPDP Act, especially with regards to exercising their rights, including:
- complying with other applicable laws and their provisions
- not impersonating another person while providing personal data for a specific purpose
- not suppressing any material information while providing personal data for documents, proof of identity, proof of address, etc.
- issued by the State
- not registering any false or frivolous grievance or complaint with a data fiduciary or the Data Protection Board (the Board may issue
- a warning or impose costs on a complainant if a complaint brought by them is determined to be frivolous)
- providing only verifiably authentic information when exercising the right to correction or erasure
What are the conditions for valid consent under India’s DPDP Act?
Requests made to a data principal for consent to process personal data must be preceded by or accompanied by a notice from the data fiduciary providing information about:
- the personal data requested
- the purpose for processing
- how the data principal can exercise their rights
- how the data principal can make a complaint to the Data Protection Board
Valid consent must be “free, specific, informed, unconditional and unambiguous, with a clear affirmative action”. Consent signifies an agreement for processing of personal data for a specified purpose, and is limited to the personal data that is necessary to fulfill that purpose.
A data principal can withdraw their consent at any time, and it must be as easy to do so as to give consent. At the point when consent is withdrawn, the data fiduciary (or data processor) must stop processing their personal data. If requested, and if legally possible, that personal data must also be deleted.
Consent for marketing or advertising purposes
The DPDP Act does not contain specific clauses outlining requirements for or prohibiting the processing of personal data for marketing or advertising purposes for adults, including data use for targeted advertising or profiling. Targeted advertising to children is prohibited, however.
What protections are there for children’s data under the Indian personal data protection law?
A data fiduciary must obtain verifiable consent from a parent or guardian before processing any personal data from a child or person with a disability. Additionally, data fiduciaries must not track or engage in behavioral monitoring of children or targeted advertising directed at children.
India’s mobile market is huge: Top 5 privacy challenges for Apps and Games publishers in 2024
What are companies’ responsibilities under the Indian privacy law?
Entities have responsibilities on several fronts under the Act, including to data principals, with regards to the data itself, and if they engage the services of any third-party data processor, which can only be done under contract. The data fiduciary is ultimately responsible under the law for actions taken on its behalf by any data processor contracted to it, or in the event of a data breach involving the data processor. Data fiduciaries must also keep records of processing activities, including the purposes of processing, categories of data principals, and data transfers.
Legal processing of personal data
Personal data may be processed only when the data principal has given consent, or for certain legitimate uses (“legitimate interest” under the GDPR). Applications of legitimate use are significantly restricted. They include, under current Indian law:
- personal data voluntarily provided by the data principal to the data fiduciary for a specified purpose (and they have not indicated that they do not consent to the use of the data)
- processing by the state to enable issuing benefits, services, licenses, etc. when the data principal’s consent has been received before or the personal data is already available digitally in a database or other repository maintained by the State.
- fulfillment of a legal obligation, judgment, or order
- compliance with legal judgment or order relating to contractual or civil claims
- providing lifesaving medical care or in responding to a life-threatening medical emergency
- providing medical treatment or health services during an epidemic, disease outbreak, or other threat to public health
- ensuring the safety of or providing assistance or services to any individual during a disaster or breakdown of public order
- for employment or to safeguard employers from loss or liability resulting from the actions of a data principal who is an employee
Data fiduciaries’ responsibilities for personal data
Entities that collect and process personal data have several responsibilities, including:
- maintaining the completeness, accuracy, and consistency of the data
- taking reasonable technical and security measures to protect the data
- deletion of the data once the purpose for which it was collected and processed is complete
In conjunction with data principals’ rights, data fiduciaries also need to:
- provide information about personal data in their possession and about processing to data principals upon reasonable request
- correct or delete personal data when notified (with some exceptions)
- address complaints levied by data principals regarding issues relating to the data processing and the stipulations of the law
Data fiduciary notified as a Significant Data Fiduciary (SDF)
The Central Government, upon assessment, may notify a data fiduciary that they have been determined to be “significant”. This is based on factors like:
- volume and sensitivity of personal data processed
- risk to the rights of data principals
- potential impact on the sovereignty and integrity of India
- risk to electoral democracy
- security of the State
- public order
There are a number of requirements for data fiduciaries determined to be Significant Data Fiduciaries, including:
- appointing a Data Protection Officer who will represent the SDF under provisions of the DPDP Act and who is:
- based in India
- responsible to the SDF’s Board of Directors or comparable governing body
- the point of contact for the SDF’s grievance redressal mechanism under the Act
- appointing an independent audit to carry out data audits to evaluate the SDF’s compliance with the Act
- undertaking periodic data protection impact assessments (DPIA), which include:
- describing the rights of data principals
- purposes of personal data processing
- assessment and management of risks to data principals’ rights, etc.
- undertaking periodic data audits
- other prescribed measures consistent with provisions of the Act
International data transfers
The DPDP Act allows for transfers of personal data outside of India, except to countries that have been notified by the Central Government. Concerns have been expressed that this mechanism may not ensure adequate evaluation standards for data protection in the countries where data transfers are allowed.
The Central Government may notify a data fiduciary to restrict transfers of personal data for processing to a country or territory outside of India. Any Indian law currently in force will supersede the Act if it allows for a higher degree of protection for personal data, or restriction on transfers of personal data.
Privacy notice or privacy policy requirement
The Act requires that requests for data principals’ personal data be preceded by or accompanied by a notice about the personal data requested, the purpose of processing, how the data principal can exercise their rights, and how they can make a complaint to the Data Protection Board.
The Act specifies that every consent request or other notice to data principals must be presented in “clear and plain language”, and accessible in English or any constitutionally recognized language. Where applicable, contact details for a Data Protection Officer must be included, or for any other person authorized by the data fiduciary to respond to communications from data principals to exercise their rights under the DPDP Act.
The Act does not specifically reference a privacy policy or notice, e.g. as can be found on many websites.
Data Protection Officer
When required, data fiduciaries must appoint a Data Protection Officer and must publish business contact information for this person in a prescribed manner. Or they must be able to provide contact details for a person who can provide answers to inquiries and information on behalf of the data fiduciary if data principals inquire about the processing of their personal data.
Contracts with data processors
Data fiduciaries can engage data processors to process personal data on their behalf for any activity related to offering goods or services to data principals. However, this can only be done under a valid contract. Data fiduciaries are ultimately responsible for the actions of any data processors they engage.
What are the exemptions to the DPDP Act?
The Central Government may exempt government agencies from DPDP Act provisions in the interest of national security, public order, and prevention of offenses. This option includes quite a few agencies. It is possible that exempt agencies could collect, process, and retain personal data beyond what is necessary in such cases. The government can also exclude categories of organizations in the future, like startups, which raises concerns about privacy oversight.
Exemptions also include processing publicly available personal data, processing data for research purposes, and in some circumstances, processing personal data of non-Indian citizens.
Personal data exemptions
The Act does not apply to personal data processed by an individual for personal or domestic purposes, for journalistic purposes or artistic expression, or to personal data that is made or caused to be made publicly available by the data principal to whom the data relates, or any other person with an obligation under current Indian law to make that personal data publicly available.
Enforcement and penalties under India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act
The Central Government is the ultimate authority, though management and enforcement of the DPDP Act will fall to the Data Protection Board they appoint. The Act also makes it very clear what mechanisms data principals have to register complaints about personal data processing or breaches, how those must be handled and by whom, and what the potential penalties are for confirmed violations.
The DPDP Act defines a personal data breach as “any unauthorised processing of personal data or accidental disclosure, acquisition, sharing, use, alteration, destruction or loss of access to personal data, that compromises the confidentiality, integrity or availability of personal data”.
DPDP Act enforcement authorities
India’s Central Government will establish a Data Protection Board to adjudicate on issues of noncompliance with the DPDP Act. Board members and the Chairperson will be appointed by the Central Government for two-year terms and are eligible for re-appointment.
Board members will be individuals who possess “special knowledge or practical experience in the fields of data governance, administration or implementation of laws related to social or consumer protection, dispute resolution, information and communication technology, digital economy, law, regulation or techno-regulation, or in any other field which in the opinion of the Central Government may be useful to the Board, and at least one among them shall be an expert in the field of law”.
With approval from the Central Government, the Board may appoint officers and employees necessary to perform its functions under the Act. The text of the DPDP Act also notes that, the Board and the Appellate Tribunal (which handles data principal appeals of Board decisions) shall function as an independent body, and, as far as practicable, as a digital office, meaning functions like receiving complaints, making inquiries, announcing decisions, etc. should be set up digitally by design.
Submitting complaints under the India DPDPA
In addition to publishing contact information for a representative of the data fiduciary or a Data Protection Officer, data fiduciaries must establish an “effective mechanism to redress the grievances of data principals”. Typically this includes a phone number, email address, online form, etc.
A data principal can make a complaint regarding a personal data breach by a data fiduciary to the Board or to a Consent Manager (which will then liaise with the Board), which will make inquiries regarding the breach and impose penalties where relevant. The Board will make decisions regarding whether there are sufficient grounds with a complaint to proceed with an inquiry. For the purposes of inquiries, the Board will have the same powers as a civil court regarding summoning people, receiving evidence, inspecting documents, etc.
Voluntary undertaking during a complaint investigation
An entity under investigation relating to a compliance complaint under the DPDP Act can offer a voluntary undertaking at any stage of the inquiry. This is a voluntarily offered commitment to achieve compliance with DPDP Act provisions. The undertaking can include specific actions to be taken, not taken, or ceased. The data fiduciary makes this offer to the Data Protection Board, which has the authority to accept, modify, or reject it, and to make it publicly known if the entity will commence with the undertaking.
If accepted, a voluntary undertaking provides legal protection from penalties related to the alleged violation of the Act, as long as they do not fail to meet the terms of the undertaking. If they do fail to achieve compliance, the Board can impose penalties.
Appealing decisions by the Data Protection Board
If a complainant is unsatisfied with a decision by the Board, they can file an appeal within 60 days of receiving the Board’s decision. A fee may be charged for this filing. Appeals are handled by the Appellate Tribunal, and must be dealt with within six months under most cases, and if this is not possible, the reasons must be recorded.
Data breach notifications
Data fiduciaries are responsible for appropriate technical, organization, and security measures to ensure compliance with the DPDP Act and protection of any personal data in their possession. The data fiduciary is also responsible for the actions of third-party data processors contracted to it, or in the event of a data breach occurring with such a third party.
In the event of a personal data breach, the data fiduciary must notify the Data Protection Board and each affected data principal in a way determined by the Board. Upon notification of a breach or alleged breach, the Board will direct urgent remedial or mitigation measures, as well as performing inquiries regarding the breach and imposing penalties.
Penalties and fines
The Data Protection Board will have responsibility for determining penalties for violations and amounts of those penalties. Considerations for the severity of penalties imposed upon a data fiduciary will include:
- nature, gravity, and duration of the breach
- type and nature of the personal data affected by the breach
- repetitive nature of the breach
- whether the person, as a result of the breach, has realized a gain or avoided loss
- whether the person took any action to mitigate the effects and consequences of the breach, and the timeliness and effectiveness of such action
- whether the monetary penalty to be imposed is proportionate and effective (particularly regarding the need to enforce compliance with the Act and deter other violations)
- likely impact of the imposition of the monetary penalty on the person
Sums received as penalties will be credited to the Consolidated Fund of India. The schedule of monetary penalties for a breach as outlined in the DPDP Act are as follows:
| Type of Breach | Penalty |
|---|---|
| Breach in observing the obligation to take reasonable security safeguards to prevent personal data breaches | May extend to two hundred and fifty crore* rupees |
| Breach in observing the obligation to give the Data Protection Board or affected data principal notice of a personal data breach | May extend to two hundred crore rupees |
| Breach in observance of additional obligations concerning children | May extend to two hundred crore rupees |
| Breach in observance of additional obligations of a Significant Data Fiduciary | May extend to one hundred and fifty crore rupees |
| Breach in observance of the duties regarding responsibilities to data principals | May extend to ten thousand rupees |
| Breach of any term of voluntary undertaking accepted by the Data Protection Board | Up to the extent applicable for the breach in respect of which the proceedings of the Board were instituted |
| Breach of any other provision of the DPDP Act or the rules made thereunder | May extend to fifty crore rupees |
*crore = 10,000,000, so 250 crore rupees equals 2.5 billion rupees, equivalent to ~US $30 million or ~€27.7 million.
How to achieve compliance with the Indian data privacy law?
India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act brings data protections to over 17% of the world’s population, and introduces compliance requirements to businesses wanting access to very large markets since it applies extraterritorially.
Understand the law and its business applications
For organizations familiar with or already compliant with established data privacy laws like the GDPR, the DPDP Act does not bring too many diversions or surprises. However, organizations should consult with qualified legal counsel and/or a data privacy expert to ensure compliance needs are met.
The importance of consent for DPDP Act compliance
In many cases, organizations can achieve compliance by requesting data principals’ consent before collecting or processing personal data. This must be done with clear and simple language, and explain what data would be collected, for what purpose(s), what the data principal’s rights are, and how they can lodge complaints. The data must also be deleted once the purpose for processing is completed in most cases.
India’s DPDP Act draft rules released
On January 3, 2025 the draft Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) rules were released, and, shortly after, the AI Governance Guidelines Development Report was also released on January 6, 2025.
These are some of the areas that include significant updates to India’s data privacy framework in the draft rules.
Consent: Requirements to inform individuals about personal data being processed, processing purpose, and services that will be enabled, and obtaining explicit written consent to collect sensitive personal data.
Security measures: Companies must implement detailed security measures via programs and policies to protect personal data and prevent breaches. Contracts must also be in place between data controllers and third-party processors.
Data breach notices: If a breach occurs the data controller must notify the Data Protection Board and affected individuals within 72 hours of discovery (unless the DPB grants an extended deadline).
Data deletion: When an individual withdraws consent or the legal purpose for data collection and processing has been completed, personal data must be deleted. Data controllers must notify data subjects 48 hours in advance before deleting data.
Officers: Specific requirements regarding appointing a Data Protection Officer, or, where not legally required, a professional responsible for addressing data subjects’ concerns about personal data use. Information on appointed individuals must be included on companies’ websites.
Children’s personal data and consent: Verifiable consent must be obtained from a parent or legal guardian before processing a child’s personal data. Processing of personal data is banned if it is likely to cause detrimental effects to a child’s well-being, tracks or monitors their behavior, or uses advertising that targets them.
Individuals with disabilities and consent: Verifiable consent must be obtained from a parent or guardian before processing personal data of an individual with a disability if they cannot provide it personally.
Cross-border data transfers: The government may restrict or impose additional requirements for the transfer of personal data outside of India.
Consent managers: Entities registered with the Data Protection board to assist companies and data controllers with consent management for personal data processing. Consent managers must be incorporated in India and have a net worth of at least 2 crore Indian rupees (approximately USD 230,000).
No official timeline for implementation of the draft rules has been released, however, the Union Minister for Electronics and Information Technology has indicated a timeframe of two years. India’s budget for 2025-2026 increased funding for the country’s Data Protection Board.
AI Governance Guidelines Development Report
Given the current state of AI development in India, the AI Governance report recommended a regulatory approach that is principles-based and activity-focused, i.e. regulating specific AI applications, such as those relating to consumer safety, employment, and taxation rather than the entities creating and implementing such AI functions.
Generally, the subcommittee suggested a combination of voluntary commitments and standards combined with sectoral and/or risk-based regulation of AI.
India’s 2025-2026 budget also provided funding for a proposed Centre of Excellence for AI to reinforce its focus on governance and digital infrastructure.
Know what your organization needs to do to achieve DPDP Act compliance
Organizations aiming to use legitimate interest as a legal basis for data processing need to be very careful and consult legal counsel, as the use of this option is quite restricted. Some organizations will also need to engage a Data Protection Officer, and others will just need to ensure there is an easily accessible contact person for data principals to engage with regarding exercising their rights. Organizations should also ensure they have a robust data breach response process in place.
The DPDP Act and consent management
A consent manager can help with achieving and maintaining compliance, and a consent management platform like Usercentrics CMP could be a valuable tool administered by a consent manager for enabling obtaining and managing consent from data principals. The DPDP Act does apply to the use of cookies and other tracking technologies on websites and apps.
Organizations need to ensure contractual agreements are in place before engaging data processors. They need to be aware that they are responsible for the actions of third parties they have contracted, so data processing partners should be selected carefully after due diligence.
If you have questions about how India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act may affect your business, or more generally about consent management for websites and apps, we’re happy to help. Contact one of our experts!
Usercentrics does not provide legal advice, and information is provided for educational purposes only. We always recommend engaging qualified legal counsel or privacy specialists regarding data privacy and protection issues and operations.
Google announced that they are ramping up enforcement of their EU user consent policy. Join our podcast panel of expert partners to find out what this means for your business and the steps you need to take to ensure your uninterrupted use your Google services.
Listen on Spotify Watch on YoutubeWhat you’ll learn
- What is Google’s EU user consent policy?
- What are the implications of Google’s EU user consent policy for advertisers?
- Google Consent Mode basic vs. advanced
- Steps for successfully navigating Google’s requirements
Who should watch
This webinar will benefit organizations that collect and manage user data for business purposes. The key takeaways are particularly relevant for:
- digital marketers looking to optimize data visibility and improve data-driven marketing performance
- companies using Google Ads, Google Marketing Platform and Google Analytics
- companies collecting user data for marketing purposes via websites
- companies that need to comply with local privacy laws and looking for professional tools and strategies to achieve compliance
the webinar partners are BigID and DWC
Data protection and privacy regulations play a crucial role in ensuring the online security and rights of individuals. Two significant privacy regulations, particularly for organizations operating in Europe, are the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Switzerland’s Federal Act on Data Protection (FADP).
EU member states have to comply with the GDPR, and some also have their own national data privacy regulations. Switzerland is not an EU member, so the GDPR does not apply within the country, hence the need for its own such law. While both laws aim to protect personal data and privacy, there are key differences between them that businesses must be aware of, particularly if they do business in the EU and in Switzerland. In this article, we will explore the main distinctions between the GDPR and FADP and how organizations can achieve compliance with these regulations.
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data privacy law implemented by the European Union (EU) on May 25, 2018. The GDPR consists of 99 Articles and governs the processing and protection of personal data, emphasizing transparency, consent, and individual rights concerning personal data. It applies to organizations that process the data of EU residents, regardless of whether the organization is located within the EU or not. Since 2018, the GDPR has been influential on data privacy laws passed around the world, and most follow its “opt in” consent model.
What is FADP?
The Federal Act on Data Protection (FADP) is Switzerland’s data privacy law, which came into effect on September 1, 2023. The FADP replaces the previous Swiss Data Protection Act from 1992 and aligns Swiss data protection regulation with the GDPR and other European laws. The FADP is not quite the Swiss GDPR, however, and there are differences in legal basis and consent requirements, among other things.
The FADP aims to ensure data flow between Switzerland and the EU while safeguarding the privacy and security of personal data. It grants new rights to Swiss citizens and imposes responsibilities on organizations regarding data privacy and protection.
Scope of application and extraterritoriality
One of the primary differences between GDPR and FADP lies in their scope of application. The GDPR applies to organizations that process the data of EU and EEA residents, regardless of the location of the organization doing the processing, i.e. they could be headquartered outside the EU. FADP is similarly extraterritorial, but only applies to processing of the data of Swiss citizens.
Legal basis and consent
The GDPR requires organizations that want to engage in data processing to have a valid legal basis to do so (Art. 6 GDPR). Legitimate interest has been a popular choice of legal basis in the past, as it enables organizations to avoid having to obtain user consent for data processing. However, newer laws are increasingly prohibiting legitimate interest as a legal basis and requiring explicit user consent.
Contractual fulfillment, compliance with legal obligation, and public interest are some other viable legal bases under the GDPR, however, organizations can be called upon by data protection authorities to prove the validity of their chosen legal basis.
The GDPR set the standard with its requirements for consent to be valid (Art. 7 GDPR), particularly that it is granted by a “clear, affirmative act” and is:
- freely given
- informed
- specific
- unambiguous
Many laws passed since have adopted this definition of valid consent, including the FADP, and data protection authorities increasingly frown on the use of dark patterns and other manipulations in order to increase user consent rates.
Under the FADP, individuals (natural persons), organizations (non-commercial entities) and businesses (commercial entities) are generally allowed to process personal data without a specific legal basis, unless the processing meets certain criteria.
Data processing for which prior consent is required under the FADP include:
- sensitive personal data
- high-risk profiling by a private person
- profiling by a federal body (government)
- data transfers to third countries where there is not adequate data protection (aka lack of adequacy agreement)
Both the GDPR and FADP, and pretty much all other data privacy laws around the world, do require data subjects (users, visitors, customers, players, etc.) be notified about data processing, with clear, accessible information about what data is collected, by whom, how it’s used, who may have access to it, what users’ rights are, how they can exercise them, etc.
Enforcement, fines, penalties
The GDPR can impose significant penalties for noncompliance. While most headlines are about giant tech companies with fines in the hundreds of million or billions, smaller organizations have been found in violation and fined as well.
Under the GDPR, organizations can face fines of up to €20 million or 2% of their global annual turnover, whichever is higher. Or, for repeated or severe violations, it can go up to €40 million or 4% of global annual turnover.
The FADP, on the other hand, imposes fines of up to CHF 250,000 against responsible individuals (~CHF 265,000) or up to CHF 50,000 against a company (~CHF 53,000) if it’s too difficult to determine a responsible individual.
The GDPR does not have provisions for individual responsibility, and neither law, like in some other countries, includes potential criminal charges. Both the GDPR and FADP, however, enable for private right of action, so a consumer could sue a company in the event of a violation.
Data breach notifications
In the event of a data breach, the GDPR makes notifications mandatory to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours (Art. 33 GDPR). If that’s not done, reasons why must be provided, e.g. the breach is unlikely to result in a risk to the rights and freedoms of natural persons. However, the controller would need to be able to prove such a claim.
Victims of a data breach, i.e. those whose personal data may be affected, must be notified without “undue delay” (Art. 34 GDPR) in most cases, and communications must be in clear, plain language.
Under the FADP, in the event of a data breach — including accidental or unlawful loss, deletion, destruction, alteration, or unauthorized access of personal data — the Federal Data Protection and Information Commissioner (FDPIC) must be notified promptly. Generally, controllers must also inform the data subject if the FDPIC requires it, or if it’s necessary for the data subject’s own safety and protection. (Within 72 hours is a fairly commonly accepted time frame for prompt notification.)
Data Protection Officer (DPO) requirement
Under the GDPR, organizations may be required to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if they meet certain criteria, such as processing large amounts of special categories or sensitive data or conducting regular and systematic monitoring of individuals on a large scale (Art. 37 GDPR).
The appointment of a DPO is recommended but not mandatory under the FADP. However, data controllers located outside of Switzerland must designate a representative within Switzerland if they regularly process large amounts of data in Switzerland/from Swiss citizens:
- in connection with offering goods or services
- with the purpose of monitoring behavior
- if the processing could involve high risk to data subjects
A representative is not the same and does not have quite the same responsibilities as a DPO, but is a central liaison for customers, employees, and data protection authorities.
Privacy notices and policies
As is nearly universal among data privacy laws, both the GDPR and FADP require that data subjects — those whose personal data would be collected and processed — be informed about the processing, who’s doing it, and what their recourse is. Typically, a privacy notice or policy is required to be displayed somewhere easily accessible, like on a corporate website. .
Under the GDPR, controllers are required to include the following information in a privacy notice (Art. 6 GDPR, Recital 39)
- identity of the data controller, whether the company or a third party
- contact details for the data controller
- identity of the data recipient and any other parties who may have access to the data
- recipient country if the data will be transferred cross-border
- purpose(s) of data collection and use
- duration of processing
- security measures taken to protect data
- categories of data collected, if relevant
- means of data collection, if relevant
- the legal basis for processing, if needed
- users’ rights regarding their personal data under the FADP, including the right to refuse or withdraw consent, and how to do so
Under the FADP, controllers are required to include the following information in a privacy notice:
- identity of the data controller, whether the company or a third party
- contact details for the data controller
- identity of the data recipient and any other parties who may have access to the data
- recipient country if the data will be transferred cross-border
- purpose(s) of data collection and use
- categories of data collected, if relevant
- means of data collection, if relevant
- the legal basis for processing, if needed
- users’ rights regarding their personal data under the FADP, including the right to refuse or withdraw consent, and how to do so
Data transfers
It is commonly recognized that not all countries take equal and appropriate measures to keep personal data secure and respect individuals’ privacy. Where two countries or regions recognize each other’s policies and procedures to be sufficient, they are deemed adequate and one will often see references to an adequacy agreement in place between them, like with the EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework between the EU and United States. When there is mention of a “third country”, it is often in reference to a country without an adequacy agreement, which often requires additional safeguards or explicit consent before any data can be processed by or transferred to such a country.
Both the GDPR and FADP regulations address the issue of international data transfers. The GDPR requires organizations to ensure that personal data transferred to countries outside the EU has an adequate level of protection or falls under appropriate safeguards, such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCC) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCR). Similarly, the FADP requires organizations to have adequacy agreements or obtain consent from data subjects for international data transfers.
Privacy compliance and consent management
The GDPR requires consent from users in more cases than the FADP. However, where consent is needed, requirements for both are clear and fairly stringent. Data controllers not only need to obtain consent compliantly with each regulation, but need to be able to securely store consent information, enable users to change or withdraw it in the future, or prove consent in the event of an audit by data protection authorities.
For consent management and the notification requirement (e.g. privacy policy), a consent management platform like Usercentrics CMP is an important tool. A CMP helps organizations collect and manage valid user consent, customize banners and privacy notices, and provide transparency to users about data usage. With geolocation functionality, it can also enable organizations to present the correct regulatory information to users depending on their location (and in their preferred language), to enable compliance with the GDPR and/or the FADP, for example.
A CMP also securely stores consent information so users can update their preferences or so it can be provided to users in the event of a data subject access request or audit by authorities.
Digital Markets Act applications
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) applies directly to the seven big tech companies that the European Commission designated as gatekeepers. However, to achieve compliance, the gatekeepers will apply compliance requirements to third-party companies that use their platforms and services, e.g. for advertising.
Parts of the regulation deal with data protection and user privacy, which align with the GDPR and FADP, particularly since the DMA applies to organizations with EU/EEA digital operations.
The DMA requires valid user consent to be obtained in many cases by controllers, which includes both the gatekeeper companies and third parties that rely on their platforms and services. Valid user consent uses the model common to the GDPR and FADP.
This consent must also be signaled to gatekeepers that require it, like Google, to ensure consent has been obtained before users’ personal data is collected and they receive personalized advertising or targeting in certain cases. Usercentrics CMP enables consent signaling, e.g. with Google Consent Mode.
Because most of the gatekeeper companies are located in the US (Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, Meta, and Microsoft), companies should also be aware of potential international data transfers when using these platforms and services, and ensure data privacy operations and consent management per GDPR and/or FADP requirements are in use.
GDPR and FADP summary comparison
| Requirement | GDPR | FADP |
|---|---|---|
| Penalties | Less severe violations: 2% of global annual revenue or €10 million.
More severe violations: 4% of global annual revenue or €20 million. | Up to CHF 250,000 against responsible individuals, or up to CHF 50,000 against the company if it is too difficult to determine a responsible individual. |
| Information requirements | Minimum content of privacy policies specified in Art. 13 GDPR. | Less required content in privacy policies. All countries to which personal data are transferred must be specified. |
| Records of processing activities | Includes all information specified in Art. 30 GDPR. | Includes list of export countries. |
| Data Protection Impact Assessments | Consult supervisory authority in cases of high risk, despite measures taken. | Can consult DPO instead of FDPIC in cases of high risk, despite measures taken. |
| Data export | European Commission determines adequacy.
Standard contractual clauses, binding corporate rules. | Swiss Federal Council determines adequacy.
EU standard contractual clauses or other binding corporate rules can be applied. |
| Data breach notification | Mandatory within 72 hours. | Mandatory as soon as possible. |
| Data Protection Officer | Mandatory. | Recommended. |
Summary of GDPR and FADP comparisons
Understanding the differences between GDPR and FADP is essential for organizations that operate in the EU/EEA and Switzerland or process the data of EU or Swiss citizens. While both regulations aim to protect personal data and privacy, they have distinct requirements and implications. While the GDPR is more strict in a number of ways and achieving compliance with that law will meet the requirements for many global privacy regulations, there are still specific requirements with the FADP that GDPR compliance operations will not meet, so good legal advice is important.
By implementing a consent management platform for robust consent management and adopting best practices for data protection and privacy, organizations can achieve compliance with GDPR and/or FADP, build user trust, and protect the rights of individuals.
Compliance with data protection and privacy regulations is ever-evolving and requires organizations to stay up to date with new and changing regulations and technologies. By prioritizing privacy and implementing robust consent management practices, organizations can navigate the complex landscape of data protection and privacy and build a foundation of trust with their users.
Usercentrics does not provide legal advice, and information is provided for educational purposes only. We always recommend engaging qualified legal counsel or privacy specialists regarding data privacy and protection issues and operations.
Learn more about the Federal Act on Data Protection (FADP)
Learn more about the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The European ecommerce market is forecasted to reach nearly $750 billion in 2027. In 2023, 78% of internet users in Europe bought goods or services online. With every online shopping search and every completed transaction, customers are creating and sharing personal data that includes, among other things:
- site searches
- products viewed
- time spent on a product page
- products added to cart
- purchase history
- credit card information
- email address
- product reviews
The collection and processing of all this customer data is governed by a number of global data privacy laws, depending on where the customer or store visitor is located. Many privacy laws are extraterritorial, and so protect the people in that law’s jurisdiction whose data is processed, regardless of where the company or other entity doing the processing is located. Online, ecommerce customers can be located anywhere in the world.
Among these laws is the Digital Markets Act (DMA), a regulation enacted by the European Commission (EC) that impacts users in the European Union (EU) and/or European Economic Area (EEA) and companies that collect data from users in these regions.
We look at how data shapes the ecommerce industry and how online stores can adapt their data privacy strategy to comply with the new consent requirements from DMA gatekeepers such as Google, with insights gathered from our partner network.
The role of data in the ecommerce industry
When a consumer visits your online store, the trail they leave behind is rich with information. Which products do they linger on? What are they searching for? Even how they got to the store and their abandoned cart tell a story about product or pricing interest that might not align with their expectations or budget.
Like every other industry, ecommerce is not immune to the rising global focus on data privacy. One approach that online shops are adopting in response to data protection regulations and consumer concerns is to rely less on third-party data and instead focus on gathering information from their own customers and website visitors. The data collected from these interactions can be highly valuable.
“The analysis of customer purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences plays a pivotal role in shaping ecommerce marketing strategies, especially in the context of personalized product recommendations. They can segment their audience based on demographics, interests, and behavior, ensuring that marketing messages reach the right people at the right time. This not only maximizes the efficiency of advertising spend but also enhances the overall relevance of the content.”
Sarah Åsgård, Web Analyst, Nexer Group
What does the Digital Markets Act change for the ecommerce industry?
The Digital Markets Act (DMA Law) applies to users located in the European Union and European Economic Area, but its impact is expected to reverberate globally given the transnational nature of the digital economy.
The DMA law is designed to regulate digital “gatekeepers” — major tech companies that serve as a gateway for businesses to reach consumers via their platforms and services, such as advertising with Google or Amazon’s Marketplace. These gatekeepers meet specific criteria that include having a strong economic position, a significant impact on the international market, and operations in multiple EU countries.
Many of the gatekeepers’ core platform services as identified — and impacted — by the DMA play a large role in connecting ecommerce brands with their customers.
Ecommerce’s most used core platform services (CPS):
- Social media platforms – TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook, as well as video streaming platform YouTube, where ecommerce brands can advertise
- Amazon Marketplace and Meta Marketplace – where online stores can list their products for sale
- Google Shopping – enables users to search for products and compare prices at different points of sale
- Google Ads, Amazon Ads, and Meta Ads – brands can set up and manage their digital advertising campaigns
- Google Search – brands can place sponsored ads
- Booking.com – online travel agency
Some of the DMA measures serve as real opportunities for ecommerce businesses to grow. As Sarah Åsgård, Web Analyst for Usercentrics’ partner Nexer Group, says, “…ecommerce brands can gain more comprehensive insights into the performance of their ads. Access to transparent data enables advertisers to understand key metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and engagement levels more accurately. This, in turn, allows for data-driven decision-making and optimization of ad campaigns.”
Stricter data collection and processing guidelines
One of the key impacts of the DMA on ecommerce businesses is the requirement to obtain explicit user consent for data processing for advertising purposes. Gatekeepers must obtain clear and informed consent from users before collecting and processing their personal data for this purpose, and some, like Google, are already making changes to their policies, which impact non-gatekeeper companies.
This focus on explicit consent means that ecommerce businesses must ensure they have robust consent management processes in place to be able to signal that consent in order to continue to access core platform services.
Changes in user profiling practices
The DMA imposes tighter restrictions on user profiling in advertising. Gatekeepers and advertisers are prohibited from combining user data from different platforms or services to create user profiles unless the end user has given specific, informed consent for this purpose. This limitation means that ecommerce businesses need to shift towards privacy-focused practices, potentially moving away from highly targeted personalized ads.
Åsgård explains how these restrictions will be felt by ecommerce businesses: “Combining data from various sources allows ecommerce brands to create more comprehensive and accurate customer profiles. Restrictions on this practice may lead to less precise targeting, making it harder to reach the right audience with personalized content and recommendations. Without a holistic view of customer behavior and preferences, ecommerce brands may struggle to tailor their advertising efforts effectively, potentially resulting in less relevant ad content for users.”
Possible solutions include investing in zero-party and first-party data collection via their own platforms, such as websites or mobile apps, and using techniques like contextual advertising that relies on the content of the web page instead of individual user profiles.
More transparent access to data
With transparent data about marketing performance, ecommerce brands can refine and optimize their targeting strategies. Independent verification of ad performance fosters a sense of accountability and transparency between advertisers and the platform. Åsgård explains why: “…ecommerce brands can trust the accuracy of the data provided, ensuring that their advertising investments are yielding the expected results. This increased transparency can strengthen the overall trust between advertisers and platform providers.”
Hilda Ahlqvist, Digital Analytics Specialist at Nexer Group, adds: “Advertisers can allocate their budgets more strategically based on verified performance data. With a deeper understanding of which channels and campaigns drive the best results, ecommerce brands can distribute their advertising budgets more efficiently to maximize ROI.”
Non-discrimination and fair competition
Under the DMA, gatekeepers’ online marketplaces, like Amazon Marketplace and Google Shopping, are required to treat all advertisers equally. This means they cannot prioritize their own services or products in search rankings or ad placements. The aim is to create a more competitive online advertising ecosystem where businesses with smaller budgets have equal opportunities to compete.
Ahlqvist provides some tips on how ecommerce businesses can take this opportunity to stand out: “Ensure that your online store and product listings are optimized for mobile users, considering that many customers shop on mobile devices. Implement a responsive design and utilize a mobile-friendly banner to communicate important information. A seamless and user-friendly mobile experience can positively impact your brand’s visibility and conversion rates, enhancing the overall customer journey.”
The DMA also prohibits gatekeepers from using data collected from business users and their customers when they are competing with those same businesses. This could include a wide variety of data, such as web analytics, search terms, social media engagement, and purchase trends. There is an exception for data that is publicly available, since the gatekeepers don’t acquire this data from the businesses’ use of their platforms.
Interoperability between platforms
The DMA mandates that gatekeepers allow third parties to inter-operate with their services, enabling users to switch between different platforms. Data portability is also an increasingly common right that consumers have under international privacy laws.
Smaller, independent marketplaces are perfectly placed to make the most of this DMA requirement. They have the opportunity to integrate with core platform service marketplaces such as the ones by Amazon and Meta, opening the door to a wider target audience, improved user experience, and potentially higher conversions.
This opportunity also comes with some challenges. Smaller ecommerce brands and marketplaces will need to navigate technical, commercial, and regulatory challenges when integrating with larger platforms, which could lead to increased costs for implementation and maintenance.
Google’s new consent requirements
As one of the seven gatekeepers under the DMA, Google has been preparing for the new rules to come into force in March 2024, and adjusting their EU user consent policy accordingly.
For its publisher products, Google has announced that companies using Google AdSense, Ad Manager or AdMob must use a Google-certified consent management platform (CMP) to serve ads to users in the EU, EEA and the United Kingdom from January 16, 2024 on (with enforcement starting on February 1, 2024). This enables brands to collect explicit consent under the requirements of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which aligns with the DMA’s consent requirements.
With the aim of combining data protection and marketers’ (advertisers) interests, Google has also announced that use of Google Consent Mode v2 will be mandatory from March 2024 for all websites using Google Analytics (including GA4), Google Ads (Google Ads Conversion Tracking and Remarketing), Floodlight and Conversion Linker. Their latest help article came to reinforce this deadline.
In other words, the best way to keep promoting your online store and products when using the Google services mentioned above is to combine a certified consent management platform like Usercentrics with Consent Mode v2.
With valid consent collection from website users and customers, you can continue to optimize opt-ins, measure conversions and retrieve analytics insights with Google Consent Mode, while achieving and maintaining GDPR compliance.
Read about consent mode GA4 now
How ecommerce businesses can use consented data to create better customer experiences
Conveniently, the same tools that enable ecommerce companies to achieve data privacy compliance and continue monetizing with Google services also enable them to provide users with great customer experiences when requesting access to personal data.
Implement a Google-certified consent management platform (CMP)
Implementing a consent management platform like Usercentrics CMP or Cookiebot consent management platform (CMP) can streamline the process of obtaining consent from your shoppers. Both Usercentrics CMP and Cookiebot CMP also support Google Consent Mode and are Google-certified CMPs, enabling you to display ads to users in compliance with data privacy laws.
“Usercentrics’ integrations are simple plug-and-play solutions that enable our mutual customers to comply with global privacy laws and data protection regulations. It builds user trust by creating a transparent user experience with clear information.”
– Mandy Engel, Technology Partner Manager – Acquisition Specialist, Shopware
Usercentrics’ consent management platforms are designed to integrate smoothly with ecommerce platforms such as Shopify, Shopware, PrestaShop and BigCommerce, as well as Stripe for payment processing.
Usercentrics App CMP also provides full support for apps developed on iOS, Android, React, and Flutter, ensuring that you can also obtain valid consent across your online shopping apps.
Strategies to optimize consent rates
Enhance your consent rates by making the process transparent and user-friendly, fostering trust and willingness among customers to share their data.
Demonstrate clear value: Clearly communicate how customer data will be used, users’ options for providing or changing consent preferences, and the benefits of sharing their data. By illustrating how data sharing can lead to personalized shopping recommendations or exclusive discount offers, customers may feel more inclined to consent.
Simplify the consent process: Making it easy for customers to give consent can lead to higher consent rates. Aim for consent tools and user interfaces that are straightforward and user-friendly, including clear and concise opt-in forms or cookie consent banners written in straightforward language, are designed to avoid any manipulative design techniques.
Build trust: Employing design principles that present users with genuine choice to opt in demonstrates respect for customer privacy. Customers, in turn, feel their data is valued and treated with respect, not just used as a tool for aggressive marketing.
For more in-depth tips on how to boost opt-ins and consent rates on websites and apps to get the high quality data you need for your marketing strategy, check out our white paper: Optimizing consent data and user trust.
Read about cookie consent tips now
Using consented data for pay-per-click (PPC) advertising
Ecommerce businesses can leverage consented data to enhance customer experiences and optimize their PPC advertising strategies. Using tools like Google Consent Mode in Google Ads, businesses can comply with regulations while still accessing valuable insights for campaign optimization.
Conversion modeling, audience building, and performance tracking are all key components that, when used effectively, maximize results and optimize ad spend in a privacy-conscious advertising landscape.
Conversion modeling with Google Ads
- Consented data for modeling: With conversion modeling in Google Ads, ecommerce businesses can fill in the measurement gaps when users do not consent to cookies. The system uses Google AI to assess attribution paths for unconsented journeys, using observable data and historical trends.
- Optimizing bidding: Modeled conversions are integrated into Google Ads reports, impacting bid strategies such as Target CPA or Target ROAS. Businesses can optimize campaigns based on a more complete view of conversion data.
Creating remarketing lists
- Audience exclusions: While cookieless pings cannot be used to create remarketing lists, consented data allows for the formation of these lists. This helps in targeting users who have shown interest in certain products or services.
- GA4 audiences: Google Analytics 4 allows ecommerce businesses to create audiences based on consented user interactions (using the GA4 audience builder tool). These audiences can be used for targeted advertising within Google Ads.
Optimizing ad spend with Consent Mode
- Advanced Consent Mode implementation: By choosing advanced implementation, tags send cookieless pings when consent is declined, enabling Google to provide modeled data for GA4 properties. This helps in retaining insights for optimization despite the lack of consent. Combining it with Usercentrics CMP’s Analytics Dashboard and A/B Testing feature will get you even more insights to optimize user consent for data collection.
- Impact on performance: The use of consented data and conversion modeling may impact the performance reported in Google Ads. However, these models aim to minimize over-prediction, ensuring that ad spend is optimized based on the most accurate data available.
Best practices for ecommerce PPC with Consent Mode
- Implement Consent Mode: Ensure that tags are loaded and send cookieless pings when consent is denied. This enables behavioral and conversion modeling to fill data gaps.
- Consent Management Platform (CMP): Integrate Consent Mode with a CMP like Usercentrics CMP for web or mobile apps for efficient management of user consents across marketing channels.
- Monitor and adapt: Regularly test, validate, and update your Consent Mode implementation to align with evolving privacy regulations and Google’s documentation.
Read about cookieless attribution now
Monitoring campaign performance
- Reporting and bidding implications: The consent modeling data will appear in the “Conversions” and “Conversion value” columns in Google Ads, affecting all reports that use these metrics. This integration aids in informed decision-making for ad spend adjustments.
- Performance maximization: Ecommerce businesses should revisit their bidding strategies after the launch of conversion modeling to ensure optimized performance and ROI.
Stay updated on regulatory developments and gatekeeper requirements
Gatekeepers are required to comply with the Digital Markets Act’s requirements by March 6, 2024. As the date comes nearer, other gatekeepers may require businesses that use their platforms to make certain changes to align with the DMA or future laws.
The European Commission may also designate additional large tech companies as gatekeepers, and additional offerings as core platforms services.
Google could also implement further future adjustments to their EU user consent policy or the existing privacy requirements we’ve described above.
A good way to stay up to date is to receive relevant updates by subscribing to our newsletter to get the latest privacy news straight to your inbox.
Seek expert advice
Whether you need to help with technology implementation, data management processes, setting up compliant analytics or assessing your legal compliance, a good place to start is our global partner network directory.
The European Digital Markets Act (DMA) is a landmark piece of legislation aimed at promoting fair and competitive digital markets in the European Union. The DMA law sets out a framework for regulating large tech companies, known as gatekeepers, to ensure they do not abuse their market power and to protect user privacy and consent online.
This framework will impose a significant shift for key players in ad tech – the gatekeepers – who will now be accountable to ensure the data they collect has proper user consent, whereas in the past this was the responsibility of the websites that used the gatekeepers’ services.
In this article, we’ll provide a Digital Markets Act summary, exploring the key provisions and the DMA’s impact on organizations and users in the digital space.
What is the Digital Markets Act or DMA law?
The Digital Markets Act (DMA), which came into force on November 1, 2022, is designed to impact competition – namely antitrust issues – consumer protection, and privacy in the digital sector by regulating large online platforms – the gatekeepers.
The DMA imposes restrictions on social networks, search engines, video-sharing platforms, operating systems, cloud computing services, and online advertising services owned by large digital corporations. Because they have a significant impact on the market, these gatekeepers are subject to specific obligations and restrictions to level the playing field for smaller businesses and protect user rights.
For users, it enhances privacy by imposing new data restrictions and allowing them to uninstall preloaded applications.
Benefits of the Digital Market Act (DMA)
Innovators and technology start-ups will have new opportunities to compete and innovate in the online platform environment without having to comply with unfair terms and conditions limiting their development.
Consumers will have more and better services to choose from, more opportunities to switch their provider if they wish so, direct access to services, and fairer prices.
Businesses who depend on gatekeepers to offer their services in the single market will have a fairer business environment.
Gatekeepers will keep all opportunities to innovate and offer new services. They will simply not be allowed to use unfair practices towards the business users and customers.
Who are the gatekeepers under the DMA privacy law
So, who exactly are the gatekeepers? The term gatekeepers refers to the big players in the digital market, such as online platforms and search engines, that have a significant impact on the market and act as intermediaries between businesses and consumers.
The seven gatekeepers designated by the European Commission (EC) under the DMA law are:
- Alphabet
- Amazon
- Apple
- Booking.com
- ByteDance
- Meta
- Microsoft
In its press release, the EC identifies 23 core platform services overseen by these gatekeepers:
- 4 social networks (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, TikTok)
- 2 large communication services (Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp)
- 6 so-called “intermediation” platforms (Amazon Marketplace, Google Maps, Google Play, Google Shopping, iOS App Store, Meta Marketplace)
- 1 search engine (Google)
- 2 web browsers (Chrome and Safari)
- 3 online advertising services (Amazon, Google, and Meta)
- 3 most popular operating systems (Google Android, iOS, Windows PC OS)
- 1 video sharing platform (YouTube)
- 1 online travel agency (Booking.com)
DMA law: Gatekeepers’ obligations
Under the DMA, original gatekeepers had until March 6, 2024, to comply with the full list of do’s and don’ts to ensure fair competition and protect user privacy. As Booking.com was not designated until May 2024, it has until November 2024 to comply. These include avoiding unfair practices, providing transparent access to services, and sharing data with business users.
Gatekeepers’ reactions to the EC nomination
Google has already mentioned they plan to make changes, saying,
“Our goal is to implement modifications that align with the new regulations, while preserving the user experience and delivering valuable, innovative, and secure products for European users” (source: blog.google).
Microsoft accepted its gatekeeper designation, but requested to initiate an investigation into potentially exempting Microsoft’s services such as Bing, Edge, and Microsoft Ads from the DMA.
Apple and TikTok were less welcoming. Apple expressed ongoing concerns regarding DMA privacy and security risks associated with the DMA law (source: Reuters). In a statement, Apple emphasized its commitment to “mitigate these impacts and continue to deliver the very best products and services to our European customers.” TikTok said it “fundamentally disagreed with this decision” and was “disappointed that no market investigation was conducted prior to this decision,” adding it was considering its next steps.
Meanwhile, Meta, the parent company of Facebook and Instagram, launched in October a subscription model for no ads in Europe, “in response to a number of evolving and emerging regulatory requirements in the EU/EEA region”.
Interoperability and non-discrimination
Gatekeepers must ensure interoperability with third-party services, allowing them to communicate and integrate with the gatekeeper’s platform. This promotes competition and prevents gatekeepers from favoring their own services over those of competitors. Non-discrimination obligations ensure that gatekeepers treat all businesses and users fairly, without giving preferential treatment to their own products or services.
Data portability and access
Gatekeepers must enable users to transfer their personal data from one service to another, known as data portability. This allows users to switch between platforms and maintain control over their data. Gatekeepers are also required to provide real-time access to the data generated by users on their platform to businesses and third parties, upon request.
Transparency and profiling
Gatekeepers must provide a clear and audited description of the techniques used for profiling consumers on their platform. This includes information about the purpose, duration, and impact of profiling, as well as steps taken to seek user consent or provide options for denying or withdrawing consent. Transparency ensures that users are aware of how their data is being used and gives them greater control over their privacy.
DMA advertising: Pricing and measurement tools for advertisers and publishers
In addition to its focus on fair competition and user privacy, the DMA law also includes provisions related to DMA advertising. These provisions aim to ensure transparency and accountability in the advertising ecosystem. Two key articles in the DMA address the needs of advertisers and publishers:
Pricing information for advertisers and publishers
Under this article, gatekeepers are required to provide clear and transparent pricing information to advertisers and publishers. This ensures that all stakeholders have access to relevant information about advertising costs, allowing for informed decision-making and fair competition. Advertisers and publishers can rely on this information to plan and optimize their advertising strategies effectively. (Source: DMA recital 45; article 5.9)
Measuring and verification tools for advertisers and publishers
Article 6(g) of the DMA focuses on measurement and verification tools. Gatekeepers are mandated to provide advertisers and publishers with access to reliable and independent tools for measuring and verifying the performance of their advertising campaigns. This helps to establish trust and accountability in the advertising ecosystem, allowing stakeholders to assess the effectiveness and impact of their advertising efforts accurately. (Sources: DMA article 6.8; Annex A.1)
DMA advertising: impact beyond gatekeepers
While the Digital Markets Act (DMA) primarily targets the seven designated “gatekeeper” companies, it’s important to recognize that the impact extends beyond them. All companies operating digitally within the EU and relying on the platforms and services of these tech giants will also be affected.
For these companies, the DMA represents a significant wake-up call. It introduces the fundamental principle: no consent, no revenue. Compliance entails obtaining explicit consent from users before processing their personal data. However, the requirements go further. Gatekeepers are likely to demand that companies utilizing their services for advertising, e-commerce, analytics, and more adopt consent management processes that align with DMA regulations.
Non-compliance with the DMA poses a substantial financial risk for gatekeepers. Yet, third-party companies face equally significant consequences. Failing to comply could result in the loss of valuable data, audience, revenue, and brand reputation. Access to the user base, data, and services provided by gatekeepers such as Google, Meta, and others would be at stake.
Read more on our press release: Ad revenue at stake: Get ready for Digital Markets Act (DMA) compliance
DMA privacy law: Impact on user privacy and consent management
The DMA has significant implications for user privacy and consent management. It introduces restrictions on the legal bases gatekeepers can rely on to process personal data, limiting them to specific legal grounds such as user consent, legal obligations, vital interests, or tasks in the public interest.
The DMA’s focus on obtaining explicit consent aligns with the principles of consent marketing, which emphasizes obtaining permission from individuals before using their personal information for marketing purposes. By requiring explicit user consent when processing personal data, the DMA safeguards user privacy and ensures that individuals have the power to decide how their data is used.
Relying on user consent
Gatekeepers must obtain user consent for processing personal data in certain cases, such as for online advertising purposes or combining personal data from different services.
The DMA law outlines requirements for obtaining valid consent, including informing users of the consequences of not giving consent and prohibiting deceptive practices (dark patterns) that manipulate users into giving consent.
Sharing personal data
The DMA mandates that gatekeepers share personal data with businesses operating on their platform and with advertising companies, upon request. This allows businesses to access and use user data to provide personalized services and targeted advertising.
Read about consent for ads personalization now
However, gatekeepers must ensure that data sharing is done on fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory terms, protecting user privacy and preventing misuse of personal data.
Data portability rights
One of the key provisions of the DMA law is the requirement for gatekeepers to enable data portability, allowing users to transfer their personal data to other platforms or services. This empowers users to exercise greater control over their data and facilitates competition by enabling users to switch between platforms without losing their data.
Transparency and user control
Transparency is a fundamental aspect of the DMA, ensuring that users are informed about how their data is processed and giving them the ability to make informed choices.
Gatekeepers must provide clear information about their profiling techniques and obtain user consent for targeted advertising. Users should have the option to deny or withdraw consent and should not be subjected to deceptive practices.
Consent management platforms and compliance
The DMA law mandates gatekeepers to ensure websites and/or companies using their services to collect, manage, and record user consent in a transparent and user-friendly manner. How gatekeepers will achieve this and which legal and technical requirements they will define for advertisers is yet to be determined.
However, we can already understand that users of gatekeepers’ services (e.g. websites, apps and the companies behind those) will play a pivotal role in collecting appropriate consents, even if they’re not the ones ultimately liable for DMA privacy compliance.
Consent management platforms (CMP) like Usercentrics CMP or Cookiebot™ consent solution are already indispensable for businesses to collect appropriate consents for data collection.
As an important part of the DMA privacy ecosystem and the owner of both consent management solutions mentioned earlier, Usercentrics will closely monitor future developments and work to ensure that our solutions remain in line with the implications of the Digital Markets Act (DMA) and other relevant legislation that may emerge or evolve.
Challenges and future implications
While the DMA law aims to protect user privacy and promote fair competition, it also presents challenges for gatekeepers and regulators. Gatekeepers will need to adapt their data processing practices, implement technical changes, and ensure compliance with the DMA’s provisions. Regulators will play a crucial role in enforcing the DMA and ensuring that gatekeepers adhere to their obligations.
Final thoughts: Digital Markets Act and the digital ecosystem
The Digital Markets Act represents a significant step towards protecting user privacy and promoting fair competition in the digital sector. By imposing obligations on gatekeepers and enhancing user control over personal data, the DMA law aims to create a more transparent and user-centric digital ecosystem.
As gatekeepers and regulators navigate the implementation of the DMA privacy law, it’s essential to strike a balance between competition, innovation, and user privacy rights.
We’ll make sure to keep you informed about DMA privacy changes as they happen. If you want to receive digital markets act summary updates on matters of consent management straight to your inbox, make sure to subscribe to our newsletter.
Read about DMA consent now
Usercentrics does not provide legal advice, and information is provided for educational purposes only. We always recommend engaging qualified legal counsel or privacy specialists regarding data privacy and protection issues and operations.
The Google EU user consent policy is a component of online data privacy compliance requirements for businesses that use Google’s services in the European Union and European Economic Area. The policy aligns with the requirements set forth by two significant European privacy laws: the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the ePrivacy Directive. Additionally, the policy takes the Data Protection Act into account, which is the UK’s equivalent regulatory implementation to the GDPR.
Google introduced the EU user consent policy in 2015, with a significant update on May 25, 2018 when the GDPR came into force.
This policy is especially significant in digital advertising. For marketers and pay-per-click specialists, it sets the foundation for responsible data handling, ethical marketing practices, respect for user privacy, and building trust in digital markets.
We explore who the EU user consent policy applies to, what its requirements are, and how to take corrective steps if you’ve received a notice of noncompliance from Google.
Read about wordpress cookie consent now
Who does the EU user consent policy apply to?
The Google EU user consent policy applies specifically to data collected from end users located in the European Union (EU), European Economic Area (EEA), and/or the United Kingdom (UK), if the business collecting the data:
- has an agreement with Google that includes the policy
- uses Google products that incorporate the policy
A common misconception is that businesses outside the EU, EEA and/or UK don’t need to comply with the policy. The EU user consent policy applies to end users located in these regions, regardless of where the business aiming to collect their data is based.
Google’s advertising and measurement products and services, including AdSense, AdManager, AdMob and Google Analytics Advertising Features, require businesses to meet the specifications of this policy.
Other Google products that come under the scope of this policy are Google Maps Platform Terms of Service, the YouTube API Services Terms of Service, the reCAPTCHA Terms of Service, and in Blogger.
The EU user consent policy impacts websites and apps that meet two specific criteria:
- they use cookies or other local storage where legally required
- they collect, share, and use personal data for ad personalization
Google defines ads as personalized when they rely on previously collected or historical data to influence ad selection. This encompasses factors like a user’s past search queries, online activity, site or app visits, demographic details, and location.
If a website or app serves non-personalized ads using only contextual information, but uses cookies or mobile identifiers where legally required, this policy still applies.
Learn why a Google-certified CMP like Usercentrics is essential for serving ads in the EU and EEA
Requirements for Google business users under the EU user consent policy
Google has separate requirements under the policy based on who is collecting the data, which it defines as “properties under your control” and “properties under a third party’s control”.
If you use a Google product and this results in the sharing of a third party’s end-user personal data with Google, you must employ “commercially reasonable efforts” to ensure that the third party adheres to this policy.
For properties that are under your control, or under the control of an affiliate or client, Google has laid out several requirements.
1. Obtaining legally valid consent
Legally valid consent under the GDPR (Art. 7) means users must actively agree to the collection and use of their personal data. Under both the GDPR and the Data Protection Act, consent should be freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous (Recital 32). Explicit consent is valid consent under the applicable data privacy laws.
Learn how to obtain GDPR-compliant consent from users on our blog: 7 Criteria for a GDPR-compliant Consent
2. Retaining consent records
Businesses must keep detailed records of how and when consent was obtained from users. Google has specified that, at a minimum, this includes documenting the text and consent choices presented to users, and the date and time when users gave their consent.
3. Providing clear instructions for revocation of consent
Users must be informed about how they can withdraw their consent to receive personalized ads. Minimum expectations include having easy access to ad controls on the website or app, or through general settings provided by Google or on their device.
4. Identifying each party involved in data handling
The user consent policy mandates the identification of every party that has access to the user’s personal data as a result of using a Google product, including in the collection, reception, or use of personal data.
There must also be transparent and accessible information regarding how each party uses personal data.
What happens if you don’t comply with the EU user consent policy?
Noncompliance with Google’s EU user consent policy carries significant consequences that affect both the operation of websites and apps and their broader legal standing.
Suspension of Google services or termination of agreement
Google reviewers regularly visit websites and apps that use its advertising services to assess whether they are providing clear information and obtaining proper consent as per the policy guidelines. If a website or app is found to be noncompliant, it will receive a notification from Google with a deadline to rectify these issues.
Failing to address the concerns within this period can lead to more severe measures. Google may suspend the noncompliant entity from using its advertising services, which can significantly affect its ability to generate revenue through these channels.
Websites or apps that have received a noncompliance notice must take corrective measures to comply with the policy. Among these measures is using a consent management platform (CMP), which can help you:
- obtain legally valid consent as per the policy’s consent requirements
- securely store and maintain records of consent that the policy requires
- identify and communicate information about all parties with access to user data
- provide clear and accessible mechanisms for users to withdraw consent
Legal and financial ramifications of noncompliance
Noncompliance with the EU user consent policy also poses a significant risk under the GDPR and/or Data Protection Act, including incurring substantial penalties for not obtaining compliant consent.
For first-time or less severe infractions, penalties can be as high as €10 million or 2% of the company’s global annual revenue for the preceding financial year. For repeat violations or more severe breaches, penalties may escalate to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
Find out how to meet Google’s EU privacy requirements with Usercentrics CMP.
How Usercentrics can help enable compliance with the EU user consent policy
In a move that specifically impacts digital advertising, Google announced on May 16, 2023 that publishers and advertisers using Google AdSense, Ad Manager, or AdMob must use a certified consent management platform that integrates with the Interactive Advertising Bureau’s (IAB) Transparency and Consent Framework (TCF) v2.2 as of January 16, 2024 to serve ads to end users in the EU/EEA and UK.
A Google-certified CMP enables websites and apps to comply with the EU user consent policy’s requirements, including obtaining legally valid user consent, enabling revocation of consent, and disclosure about collection and use of personal data.
Usercentrics’ consent management platform (CMP) was among the first certified CMPs when Google launched its CMP Partner Program for Google Consent Mode in September 2022. All our CMP products—Usercentrics Web and App CMPs and Cookiebot CMP—are certified by Google for this purpose.
Here’s how Usercentrics CMP makes Google consent compliance simpler and more effective.
1. Simplifying consent collection
Usercentrics CMP streamlines securing legally valid end-user consent. It enables obtaining GDPR-compliant consent with explicit opt-in and granular consent mechanisms, and full consent banner customization.
2. Easy consent withdrawal options
Usercentrics CMP enables your website or app users to update or revoke their consent just as easily as they gave it. This aligns with the user consent policy’s specific requirement of consent withdrawal options for users.
3. Transparent data usage information
With Usercentrics CMP, you can identify, for each of your websites and apps, all parties that may collect, receive, or use personal data, and lay out how and why data is being used as per the policy’s requirements for sharing clear information about the use of personal data.
4. WordPress plugin and content management system (CMS) integrations
Usercentrics CMP offers seamless integrations, including a dedicated WordPress Plugin, which simplifies implementation and consent management for WordPress-powered websites.
Other CMS and ecommerce platform integrations include Adobe Experience Manager, Shopify, Typo3, among others.
Besides CMS systems, Usercentrics integrates with a variety of ecommerce marketing tools, like Stripe, Zapier or HubSpot. This simplifies managing consent across different websites and online services.
5. Google platform integrations
For businesses using Google products and services, such as AdSense, AdManager, AdMob, Google Analytics 4 (GA4), Google Consent Mode, and Google Tag Manager, Usercentrics CMP seamlessly integrates with these platforms. This makes it easy to set up and use without disrupting advertising campaigns and analytics.
Read about consent mode GA4 now
6. Access to a partner network
For additional support, Usercentrics offers a global partner network that serves as a valuable resource for prospects and customers.
Connect with marketing agencies and legal service providers that implement, maintain, optimize and support the Usercentrics Web and App CMPs. This network provides an extra layer of support for navigating the complexities of data privacy compliance.
7. Free trial option
Curious about how Usercentrics CMP can help you continue using the Google products you love and depend on, while maintaining compliance with privacy regulations and Google’s own consent policy? What better way to explore our platform capabilities than through a free trial?
This 30-day trial period will grant you full access to all advanced features in the Starter Plan, as well as full access to ticket support, guides, and documentation. The trial expires automatically after 30 days so there’s zero risk and no commitment required from your side upfront.
8. Demos and consultations
If you’re looking for more in-depth information or personalized guidance, you can choose to book a demo or an expert consultation and have all your consent management questions answered. We want you to have a better understanding of how Usercentrics CMP can be tailored to your specific data privacy compliance and business requirements.
A practical guide for complying with the Google EU user consent policy
The easiest way to comply with the Google EU user consent policy, GDPR, and other privacy regulations is through a consent management platform. Use Usercentrics consent management platform (CMP) with your website or app to enable:
- compliance with the GDPR, DMA, CCPA, and other privacy laws
- application of privacy requirements based on user geolocation
- obtaining consent before your or third-party scripts load
- platform flexibility for desktop and mobile devices, as well as for mobile apps, games and connected TV apps.
- consent banner customization to match your brand style
You can also create a privacy policy for your website or app easily through our dynamic privacy policy generator. With this integration with Termageddon, you’re able to set up your Privacy Policy, Terms of Service, and other policies in less than 30 minutes.
For more on how to generate comprehensive and easy to understand policies, check these additional resources:
For more support resources and implementation documentation, check our support page.